Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A ball is projected from a point on the floor with a speed of 15 m/s at an angle of 60° with the horizontal. Will it hit a vertical wall 5 m away from the point of projection and perpendicular to the plane of projection without hitting the floor? Will the answer differ if the wall is 22 m away?
उत्तर
Given:
Initial speed of the ball, u = 15 m/s
The angle of projection with horizontal, α = 60°
Distance of the wall from the point of projection = 5 m
a = g = 9.8 m/s2 (Acceleration due to gravity)
We know that the horizontal range for a projectile is given by
\[R = \frac{u^2 \sin2\alpha}{g}\]
\[\Rightarrow R = \frac{{15}^2 \times \sin\left( 2 \times 60^\circ \right)}{9 . 8} = 19 . 88 \text{ m } \]
In the first case, the wall is 5m away from the projection point, so it is in the horizontal range of the projectile. So the ball will hit the wall. In the second case (22 m away), the wall is not within the horizontal range. So the ball would not hit the wall.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A car moving along a straight highway with a speed of 126 km h–1 is brought to a stop within a distance of 200 m. What is the retardation of the car (assumed uniform), and how long does it take for the car to stop?
The velocity of a particle is towards west at an instant. Its acceleration is not towards west, not towards east, not towards north and towards south. Give an example of this type of motion .
In a projectile motion the velocity
A train starts from rest and moves with a constant acceleration of 2.0 m/s2 for half a minute. The brakes are then applied and the train comes to rest in one minute. Find the total distance moved by the train .
A train starts from rest and moves with a constant acceleration of 2.0 m/s2 for half a minute. The brakes are then applied and the train comes to rest in one minute. Find the maximum speed attained by the train .
A particle starting from rest moves with constant acceleration. If it takes 5.0 s to reach the speed 18.0 km/h find the average velocity during this period .
A driver takes 0.20 s to apply the brakes after he sees a need for it. This is called the reaction time of the driver. If he is driving a car at a speed of 54 km/h and the brakes cause a deceleration of 6.0 m/s2, find the distance travelled by the car after he sees the need to put the brakes on.
Complete the following table:
| Car Model | Driver X Reaction time 0.20 s |
Driver Y Reaction time 0.30 s |
| A (deceleration on hard braking = 6.0 m/s2) | Speed = 54 km/h Braking distance a = ............ Total stopping distance b = ............ |
Speed = 72 km/h Braking distance c = ........... Total stopping distance d = ............ |
| B (deceleration on hard braking = 7.5 m/s2) | Speed = 54 km/h Breaking distance e = ........... Total stopping distance f = ............ |
Speed 72 km/h Braking distance g = ............. Total stopping distance h = ............ |
A ball is projected vertically upward with a speed of 50 m/s. Find the maximum height.
A ball is thrown at a speed of 40 m/s at an angle of 60° with the horizontal. Find the maximum height reached .
A ball is thrown at a speed of 40 m/s at an angle of 60° with the horizontal. Find the range of the ball. Take g = 10 m/s2.
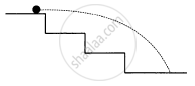
A staircase contains three steps each 10 cm high and 20 cm wide (in the following figure). What should be the minimum horizontal velocity of a ball rolling of the uppermost plane so as to hit directly the lowest plane ?
A person is standing on a truck moving with a constant velocity of 14.7 m/s on a horizontal road. The man throws a ball in such a way that it returns to the truck after the truck has moved 58.8 m. Find the speed and the angle of projection as seen from the road.
The benches of a gallery in a cricket stadium are 1 m wide and 1 m high. A batsman strikes the ball at a level one metre above the ground and hits a mammoth sixer. The ball starts at 35 m/s at an angle of 53° with the horizontal. The benches are perpendicular to the plane of motion and the first bench is 110 m from the batsman. On which bench will the ball hit?
A swimmer wishes to cross a 500 m wide river flowing at 5 km/h. His speed with respect to water is 3 km/h. Find the shortest possible time to cross the river.
An aeroplane has to go from a point A to another point B, 500 km away due 30° east of north. A wind is blowing due north at a speed of 20 m/s. The air-speed of the plane is 150 m/s. Find the time taken by the plane to go from A to B.
A ball is dropped from a building of height 45 m. Simultaneously another ball is thrown up with a speed 40 m/s. Calculate the relative speed of the balls as a function of time.
It is a common observation that rain clouds can be at about a kilometre altitude above the ground.
- If a rain drop falls from such a height freely under gravity, what will be its speed? Also calculate in km/h. ( g = 10 m/s2)
- A typical rain drop is about 4mm diameter. Momentum is mass x speed in magnitude. Estimate its momentum when it hits ground.
- Estimate the time required to flatten the drop.
- Rate of change of momentum is force. Estimate how much force such a drop would exert on you.
- Estimate the order of magnitude force on umbrella. Typical lateral separation between two rain drops is 5 cm.
(Assume that umbrella is circular and has a diameter of 1 m and cloth is not pierced through !!)
A man is standing on top of a building 100 m high. He throws two balls vertically, one at t = 0 and other after a time interval (less than 2 seconds). The later ball is thrown at a velocity of half the first. The vertical gap between first and second ball is +15 m at t = 2 s. The gap is found to remain constant. Calculate the velocity with which the balls were thrown and the exact time interval between their throw.
