Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose A and B in the previous problem change their positions in such a way that the line joining them becomes perpendicular to the direction of wind while maintaining the separation x. What will be the time B finds between seeing and hearing the drum beating by A?
उत्तर
Given:
Distance between A and B = x
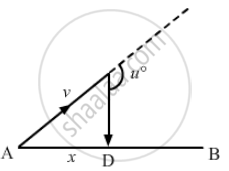
Let v be the velocity of sound in the direction along line AC.
Let u be the velocity of air in the direction along line AB.
Angle between v and u = θ > \[\frac{\pi}{2}\]
Resultant velocity of sound and air that will reach B = \[\vec{AD} = \sqrt{\left( \text{ v } ^2 - \text{ u } ^2 \right)}\]
Here, the time taken by light to reach B is neglected.
∴ Time lag between seeing and hearing = Time taken to hear the sound of the drum
\[t = \frac{\text{ Displacement } }{\text{ Velocity } }\]
\[ = \frac{x}{\sqrt{\text{ v } ^2 -\text{ u } ^2}}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A car moving along a straight highway with a speed of 126 km h–1 is brought to a stop within a distance of 200 m. What is the retardation of the car (assumed uniform), and how long does it take for the car to stop?
Two trains A and B of length 400 m each are moving on two parallel tracks with a uniform speed of 72 km h–1 in the same direction, with A ahead of B. The driver of B decides to overtake A and accelerates by 1 m/s2. If after 50 s, the guard of B just brushes past the driver of A, what was the original distance between them?
A three-wheeler starts from rest, accelerates uniformly with 1 m s–2 on a straight road for 10 s, and then moves with uniform velocity. Plot the distance covered by the vehicle during the nth second (n = 1,2,3….) versus n. What do you expect this plot to be during accelerated motion: a straight line or a parabola?
At which point on its path a projectile has the smallest speed?
In a projectile motion the velocity
A bullet travelling with a velocity of 16 m/s penetrates a tree trunk and comes to rest in 0.4 m. Find the time taken during the retardation.
A particle starting from rest moves with constant acceleration. If it takes 5.0 s to reach the speed 18.0 km/h find the average velocity during this period .
A ball is projected vertically upward with a speed of 50 m/s. Find the speed at half the maximum height. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A ball is dropped from a balloon going up at a speed of 7 m/s. If the balloon was at a height 60 m at the time of dropping the ball, how long will the ball take in reaching the ground?
A person sitting on the top of a tall building is dropping balls at regular intervals of one second. Find the positions of the 3rd, 4th and 5th ball when the 6th ball is being dropped.
A ball is thrown at a speed of 40 m/s at an angle of 60° with the horizontal. Find the range of the ball. Take g = 10 m/s2.
In a soccer practice session the football is kept at the centre of the filed 40 yards from the 10 ft high goalposts. A goal is attempted by kicking the football at a speed of 64 ft/s at an angle of 45° to the horizontal. Will the ball reach the goal post?
Find the average velocity of a projectile between the instants it crosses half the maximum height. It is projected with a speed u at an angle θ with the horizontal.
A person is standing on a truck moving with a constant velocity of 14.7 m/s on a horizontal road. The man throws a ball in such a way that it returns to the truck after the truck has moved 58.8 m. Find the speed and the angle of projection as seen from the truck .
A person is standing on a truck moving with a constant velocity of 14.7 m/s on a horizontal road. The man throws a ball in such a way that it returns to the truck after the truck has moved 58.8 m. Find the speed and the angle of projection as seen from the road.
A swimmer wishes to cross a 500 m wide river flowing at 5 km/h. His speed with respect to water is 3 km/h. If he heads in a direction making an angle θ with the flow, find the time he takes to cross the river.
A swimmer wishes to cross a 500 m wide river flowing at 5 km/h. His speed with respect to water is 3 km/h. Find the shortest possible time to cross the river.
An aeroplane has to go from a point A to another point B, 500 km away due 30° east of north. A wind is blowing due north at a speed of 20 m/s. The air-speed of the plane is 150 m/s. Find the direction in which the pilot should head the plane to reach the point B.
Two friends A and B are standing a distance x apart in an open field and wind is blowing from A to B. A beat a drum and B hears the sound t1 time after he sees the event. A and B interchange their positions and the experiment is repeated. This time B hears the drum timer after he sees the event. Calculate the velocity of sound in still air v and the velocity of wind u. Neglect the time light takes in travelling between the friends.
