Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following problem :
The probability that a bomb will hit the target is 0.8. Find the probability that, out of 5 bombs, exactly 2 will miss the target.
उत्तर
Let X denote the number of bombs hitting the target.
P(bomb hits the target) = p = 0.8
∴ q = 1 – p = 1 – 0.8 = 0.2
Given, n = 5
∴ X ~ B(5, 0.8)
The p.m.f. of X is given by
P(X = x) `""^5"C"_x (0.8)^x (0.2)^(5 - x), x` = 0, 1,...,5
∴ P(exactly two will miss the target)
= P(exactly three will hit the target)
= P(X = 3)
= `""^5"C"_3 (0.8)^3 (0.2)^(2)`
= `(5!)/(3! xx 2!)(4/5)^3 (1/5)^2`
= `(5 xx 4 xx 3!)/(2 xx 1 xx 3!) xx (4^3/5^5)`
= `10(4^3/5^5)`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A random variable X has the following probability distribution.
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| P(X) | 0 | k | 2k | 2k | 3k | k2 |
2k2 |
7k2 + k |
Determine
(i) k
(ii) P (X < 3)
(iii) P (X > 6)
(iv) P (0 < X < 3)
A random variable X ~ N (0, 1). Find P(X > 0) and P(X < 0).
Two numbers are selected at random (without replacement) from the first five positive integers. Let X denote the larger of the two numbers obtained. Find the mean and variance of X
There are 4 cards numbered 1 to 4, one number on one card. Two cards are drawn at random without replacement. Let X denote the sum of the numbers on the two drawn cards. Find the mean and variance of X.
Which of the following distributions of probabilities of a random variable X are the probability distributions?
(i)
| X : | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | −1 |
| P (X) : | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| X : | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P (X) : | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
(iii)
| X : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (X) : | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
(iv)
| X : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X) : | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| Values of X : | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X) : | 0.1 | k | 0.2 | 2k | 0.3 | k |
Find the value of k.
Four cards are drawn simultaneously from a well shuffled pack of 52 playing cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of aces.
A bag contains 4 red and 6 black balls. Three balls are drawn at random. Find the probability distribution of the number of red balls.
Three cards are drawn successively with replacement from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. A random variable X denotes the number of hearts in the three cards drawn. Determine the probability distribution of X.
An urn contains 4 red and 3 blue balls. Find the probability distribution of the number of blue balls in a random draw of 3 balls with replacement.
Let X represent the difference between the number of heads and the number of tails when a coin is tossed 6 times. What are the possible values of X?
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distributions:
| xi : | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| pi : | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution:
| xi : | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| pi: | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | -3 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| pi : | 0.05 | 0.45 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.05 |
A fair coin is tossed four times. Let X denote the longest string of heads occurring. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
A random variable has the following probability distribution:
| X = xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| P (X = xi) : | 0 | 2 p | 2 p | 3 p | p2 | 2 p2 | 7 p2 | 2 p |
The value of p is
If X is a random-variable with probability distribution as given below:
| X = xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X = xi) : | k | 3 k | 3 k | k |
The value of k and its variance are
Five bad oranges are accidently mixed with 20 good ones. If four oranges are drawn one by one successively with replacement, then find the probability distribution of number of bad oranges drawn. Hence find the mean and variance of the distribution.
Demand function x, for a certain commodity is given as x = 200 - 4p where p is the unit price. Find :
(a) elasticity of demand as function of p.
(b) elasticity of demand when p = 10 , interpret your result.
The following data gives the marks of 20 students in mathematics (X) and statistics (Y) each out of 10, expressed as (x, y). construct ungrouped frequency distribution considering single number as a class :
(2, 7) (3, 8) (4, 9) (2, 8) (2, 8) (5, 6) (5 , 7) (4, 9) (3, 8) (4, 8) (2, 9) (3, 8) (4, 8) (5, 6) (4, 7) (4, 7) (4, 6 ) (5, 6) (5, 7 ) (4, 6 )
Write the negation of the following statements :
(a) Chetan has black hair and blue eyes.
(b) ∃ x ∈ R such that x2 + 3 > 0.
A sample of 4 bulbs is drawn at random with replacement from a lot of 30 bulbs which includes 6 defective bulbs. Find the probability distribution of the number of defective bulbs.
A class has 15 students whose ages are 14, 17, 15, 14, 21, 17, 19, 20, 16, 18, 20, 17, 16, 19 and 20 years. If X denotes the age of a randomly selected student, find the probability distribution of X. Find the mean and variance of X.
There are 10% defective items in a large bulk of items. What is the probability that a sample of 4 items will include not more than one defective item?
Solve the following problem :
Find the probability of the number of successes in two tosses of a die, where success is defined as number greater than 4.
Solve the following problem :
If a fair coin is tossed 4 times, find the probability that it shows 3 heads
Solve the following problem :
A computer installation has 3 terminals. The probability that any one terminal requires attention during a week is 0.1, independent of other terminals. Find the probabilities that 0
Find the probability distribution of the number of doublets in three throws of a pair of dice
A discrete random variable X has the probability distribution given as below:
| X | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| P(X) | k | k2 | 2k2 | k |
Find the value of k
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k | `"k"/2` | `"k"/4` | `"k"/8` |
Determine P(X ≤ 2) and P(X > 2)
Two biased dice are thrown together. For the first die P(6) = `1/2`, the other scores being equally likely while for the second die, P(1) = `2/5` and the other scores are equally likely. Find the probability distribution of ‘the number of ones seen’.
Two probability distributions of the discrete random variable X and Y are given below.
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | `1/5` | `2/5` | `1/5` | `1/5` |
| Y | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(Y) | `1/5` | `3/10` | `2/10` | `1/10` |
Prove that E(Y2) = 2E(X).
Let X be a discrete random variable whose probability distribution is defined as follows:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"(x + 1), "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3"," 4),(2"k"x, "for" x = 5"," 6"," 7),(0, "Otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate Standard deviation of X.
If the p.m.f of a r. v. X is
P(x) = `c/x^3`, for x = 1, 2, 3
= 0, otherwise
then E(X) = ______.
Find the mean number of defective items in a sample of two items drawn one-by-one without replacement from an urn containing 6 items, which include 2 defective items. Assume that the items are identical in shape and size.
Find the mean of number randomly selected from 1 to 15.
A box contains 30 fruits, out of which 10 are rotten. Two fruits are selected at random one by one without replacement from the box. Find the probability distribution of the number of unspoiled fruits. Also find the mean of the probability distribution.
Kiran plays a game of throwing a fair die 3 times but to quit as and when she gets a six. Kiran gets +1 point for a six and –1 for any other number.
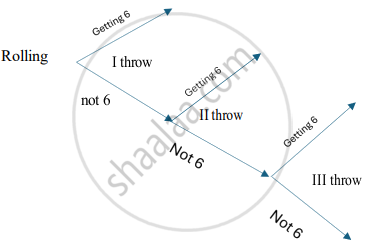
- If X denotes the random variable “points earned” then what are the possible values X can take?
- Find the probability distribution of this random variable X.
- Find the expected value of the points she gets.
