Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The conductivity of 0.20 mol L−1 solution of KCl is 2.48 × 10−2 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation (α). Given λ0 (K+) = 73.5 S cm2 mol−1 and λ0 (C1−) = 76.5 S cm2 mol−1.
उत्तर
Conductivity of KCl solution = 2.48×10–2 S cm–1
Concentration of KCl solution = 0.20 mol L–1
= 0.20 × 1000 mol cm–3
= 200 mol cm–3
Molar conductivity
`Lambda_m=k/c`
`=(2.48xx10^(-2)" S "cm^(-1))/(200" mol "cm^(-3))`
`=124xx10^(-6)" S "cm^2" mol"^(-1)`
Given:
`lambda_(K^+)^@=73.5" S "cm^2" mol"^(-1)`
`lambda_(Cl^-)^@=76.5" S "cm^2" mol"^(-1)`
Degree of dissociation
`alpha=Lambda_m/Lambda_m^@" "" "" "" ".......("i")`
`Lambda_(m(KCl))^@=lambda_(K+)^@+lambda_(Cl^-)^@`
`=73.5+76.5`
`=150" S "cm^2" mol"^(-1)`
`"Substituting the values of "Lambda_m" and "Lambda_(m(KCl))^@" in (i), we get"`
`alpha=(124xx10^(-6)" S "cm^2" mol"^(-1))/(150" S "cm^2" mol"^(-1))=0.82xx10^(-6)`
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions.
How can you determine limiting molar conductivity, 0 m for strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte?
The S.I. unit of cell constant for conductivity cell is __________.
Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions states ____________.
Why on dilution the m Λm of \[\ce{CH3COOH}\] increases very fast, while that of \[\ce{CH3COONa}\] increases gradually?
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer. Graphically show the behavior of ‘A’ and ‘B’.
The limiting molar conductivities for Nacl, KBr and KCI are 126, 152 and 150 S cm2 mol–1 respectively. The limiting molar conductivity for Na Br is:-
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
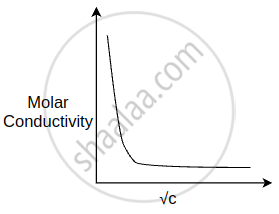
The electrolyte X is ______.
Conductivity of 2 × 10−3 M methanoic acid is 8 × 10−5 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation if `∧_"m"^0` for methanoic acid, is 404 S cm2 mol−3.
The specific conductance of 2.5 × 10-4 M formic acid is 5.25 × 10-5 ohm-1 cm-1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation.
Given `λ°_("H"^+)` = 349.5 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1 and
`λ°_("HCOO"^-) = 50.5 " ohm"^-1 "cm"^2 "mol"^-1`
