Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The dimensions of a rectangle ABCD are 51 cm × 25 cm. A trapezium PQCD with its parallel sides QC and PD in the ratio 9 : 8, is cut off from the rectangle as shown in the following figure. If the area of the trapezium PQCD is `5/6` th part of the area of the rectangle, find the lengths QC and PD.
उत्तर
Given: ABCD is a rectangle, where AB = 51 cm and BC = 25 cm.
The parallel sides QC and PD of the trapezium PQCD are in the ratio of 9 : 8. Let QC = 9x and PD = 8x.
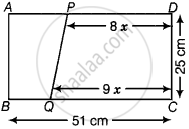
Now, the area of trapezium PQCD:
= `1/2` × (Sum of parallel sides) × (Distance between parallel sides)
= `1/2 xx (9x + 8x) xx 25 cm^2`
= `1/2 xx 17x xx 25`
Again, area of rectangle ABCD = BC × CD = 51 × 25
Now, according to the question,
Area of trapezium PQCD = `5/6` × Area of rectangle ABCD
= `1/2 xx 17x xx 25`
= `5/6 xx 51 xx 25`
x = `5/6 xx 51 xx 25 xx 2xx 1/(17 xx 25)`
x = 5
Therefore, the length of the trapezium PQCD, QC = 9x = 9 × 5 = 45 cm and PD = 8x = 8 × 5 = 40 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the values of k so that the area of the triangle with vertices (1, -1), (-4, 2k) and (-k, -5) is 24 sq. units.
If the points P(–3, 9), Q(a, b) and R(4, – 5) are collinear and a + b = 1, find the values of a and b.
The class X students of a secondary school in Krishinagar have been allotted a rectangular plot of land for their gardening activity. Saplings of Gulmohar are planted on the boundary at a distance of 1 m from each other. There is a triangular grassy lawn in the plot as shown in the following figure. The students are to sow seeds of flowering plants on the remaining area of the plot.

(i) Taking A as origin, find the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle.
(ii) What will be the coordinates of the vertices of Δ PQR if C is the origin?
Also calculate the areas of the triangles in these cases. What do you observe?
Two vertices of a triangle are (1, 2), (3, 5) and its centroid is at the origin. Find the coordinates of the third vertex.
If G be the centroid of a triangle ABC and P be any other point in the plane, prove that PA2+ PB2 + PC2 = GA2 + GB2 + GC2 + 3GP2.
Find the area of a triangle whose sides are respectively 150 cm, 120 cm and 200 cm ?
Find the value of y for which the points A(-3, 9), B(2,y) and C(4,-5) are collinear.
The table given below contains some measures of the right angled triangle. Find the unknown values.
| Base | Height | Area |
| 5 feet | ? | 20 sq.feet |
Points A(3, 1), B(12, –2) and C(0, 2) cannot be the vertices of a triangle.
Find the coordinates of the point Q on the x-axis which lies on the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the points A(–5, –2) and B(4, –2). Name the type of triangle formed by the points Q, A and B.
