Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
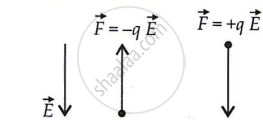
The figure shows tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field. Give the signs of the three charges. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio?

उत्तर
Opposite charges attract each other and the same charges repel each other. It can be observed that particles 1 and 2 both move towards the positively charged plate and repel away from the negatively charged plate. Hence, these two particles are negatively charged. It can also be observed that particle 3 moves towards the negatively charged plate and repels away from the positively charged plate. Hence, particle 3 is positively charged.
The charge to mass ratio (emf) is directly proportional to the displacement or amount of deflection for a given velocity. Since the deflection of particle 3 is the maximum, it has the highest charge to mass ratio.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that if we connect the smaller and the outer sphere by a wire, the charge q on the former will always flow to the latter, independent of how large the charge Q is.
The charge on a proton is +1.6 × 10−19 C and that on an electron is −1.6 × 10−19 C. Does it mean that the electron has 3.2 × 10−19 C less charge than the proton?
Why does a phonograph record attract dust particles just after it is cleaned?
In some old texts it is mentioned that 4π lines of force originate from each unit positive charge. Comment on the statement in view of the fact that 4π is not an integer.
When the separation between two charges is increased, the electric potential energy of the charges
Consider the situation in the figure. The work done in taking a point charge from P to Ais WA, from P to B is WB and from P to C is WC.
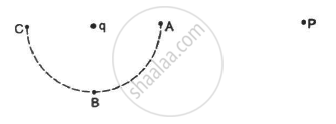
A point charge q is rotated along a circle in an electric field generated by another point charge Q. The work done by the electric field on the rotating charge in one complete revolution is
The electric field and the electric potential at a point are E and V, respectively.
Electric potential decreases uniformly from 120 V to 80 V, as one moves on the x-axis from x = −1 cm to x = +1 cm. The electric field at the origin
(a) must be equal to 20 Vcm−1
(b) may be equal to 20 Vcm−1
(c) may be greater than 20 Vcm−1
(d) may be less than 20 Vcm−1
Which of the following quantities does not depend on the choice of zero potential or zero potential energy?
A particle of mass m and charge q is thrown at a speed u against a uniform electric field E. How much distance will it travel before coming to momentary rest ?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. Find the electric force and the force of gravity acting on this particle. Can one of these forces be neglected in comparison with the other for approximate analysis?
An electric field of 20 NC−1 exists along the x-axis in space. Calculate the potential difference VB − VA where the points A and B are
(a) A = (0, 0); B = (4 m, 2m)
(b) A = (4 m, 2 m); B = (6 m, 5 m)
(c) A = (0, 0); B = (6 m, 5 m)
Do you find any relation between the answers of parts (a), (b) and (c)?
The kinetic energy of a charged particle decreases by 10 J as it moves from a point at potential 100 V to a point at potential 200 V. Find the charge on the particle.
In general, metallic ropes are suspended on the carriers taking inflammable materials. The reason is ______.
Two similar spheres having +Q and -Q charges are kept at a certain distance. F force acts between the two. If at the middle of two spheres, another similar sphere having +Q charge is kept, then it experiences a force in magnitude and direction as ______.
The Electric field at a point is ______.
- always continuous.
- continuous if there is no charge at that point.
- discontinuous only if there is a negative charge at that point.
- discontinuous if there is a charge at that point.
