Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The fourth vertex D of a parallelogram ABCD, whose three vertices are A(–2, 3), B(6, 7) and C(8, 3), is ______.
विकल्प
(0, 1)
(0, –1)
(–1, 0)
(1, 0)
उत्तर
The fourth vertex D of a parallelogram ABCD, whose three vertices are A(–2, 3), B(6, 7), and C(8, 3) is (0, –1).
Explanation:
Let the fourth vertex of the parallelogram, D ≡ (x4, y4) and L, M be the middle points of AC and BD, respectively,
Then, `L ≡ ((-2 + 8)/2, (3 + 3)/2) ≡ (3, 3)` and `M ≡ ((6 + x_4)/2, (7 + y_4)/2)` ...`["Since mid-point of a line segment having points" (x_1, y_1) "and" (x_2, y_2) = ((x_1 + x_2)/2, (y_1 + y_2)/2)]`
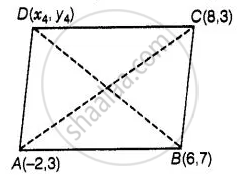
Since, ABCD is a parallelogram, therefore diagonals AC and BD will bisect each other.
Hence, L and M are the same points.
∴ 3 = `(6 + x_4)/2` and 3 = `(7 + y_4)/2`
⇒ 6 = 6 + x4 and 6 = 7 + y4
⇒ x4 = 0 and y4 = 6 – 7
∴ x4 = 0 and y4 = –1
Hence, the fourth vertex of the parallelogram is D = (x4, y4) = (0, –1).
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the coordinates of the centroid of a triangle whose vertices are (–1, 0), (5, –2) and (8, 2)
If the coordinates of the mid points of the sides of a triangle are (1, 1), (2, – 3) and (3, 4) Find its centroid
Find the coordinates of the points of trisection of the line segment joining (4, -1) and (-2, -3).
The line segment joining the points (3, -4) and (1, 2) is trisected at the points P and Q. If the coordinates of P and Q are (p, -2) and (5/3, q) respectively. Find the values of p and q.
Find the ratio in which the join of (–4, 7) and (3, 0) is divided by the y-axis. Also, find the co-ordinates of the point of intersection.
Find the coordinates of a point P, which lies on the line segment joining the points A (−2, −2), and B (2, −4), such that `AP=3/7 AB`.
Find the length of the hypotenuse of a square whose side is 16 cm.
The origin o (0, O), P (-6, 9) and Q (12, -3) are vertices of triangle OPQ. Point M divides OP in the ratio 1: 2 and point N divides OQ in the ratio 1: 2. Find the coordinates of points M and N. Also, show that 3MN = PQ.
If (a/3, 4) is the mid-point of the segment joining the points P(-6, 5) and R(-2, 3), then the value of ‘a’ is ______.
Point C divides the line segment whose points are A(4, –6) and B(5, 9) in the ratio 2:1. Find the coordinates of C.
