Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The gain factor of an amplifier in increased from 10 to 12 as the load resistance is changed from 4 kΩ to 8 kΩ. Calculate (a) the amplification factor and (b) the plate resistance.
उत्तर
We know:-
Voltage gain = \[\frac{\mu}{1 + \frac{r_p}{R_L}} ............(1)\]
When voltage amplification factor, A = 10,
RL = 4 kΩ
\[10 = \frac{\mu}{1 + \frac{r_p}{4 \times {10}^3}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 10=\frac{\mu \times 4 \times {10}^3}{4 \times {10}^3 + r_p}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 4 \times {10}^4 + 10 r_P = 4000 \mu .........(2)\]
Now, increased gain, A = 12
Substituting this value in (1) ,we get:-
\[12 = \frac{\mu}{1 + \frac{r_P}{R_L}}\]
\[12 = \frac{\mu}{1 + \frac{r_p}{8 \times {10}^3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 12 = \frac{\mu \times 8000}{8000 + r_P}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 96000 + 12 r_P = 8000 \mu ...........(3)\]
On solving equations (2) and (3), we get:-
\[\mu = 15\]
\[ r_P = 2000 Ω = 2 k\Omega\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) Explain with the help of a diagram the formation of depletion region and barrier potential in a pn junction.
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time if the input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
The graph shown in the figure represents a plot of current versus voltage for a given semiconductor. Identify the region, if any, over which the semiconductor has a negative resistance.
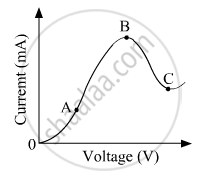
With reference to semi-conductors answer the following :
(i) What is the change in the resistance of the semi-conductor with increase in temperature ?
(ii) Name the majority charge carriers in n-type semi-conductor.
(iii) What is meant by doping ?
The dynamic plate resistance of a triode value is 10 kΩ. Find the change in the plate current if the plate voltage is changed from 200 V to 220 V.
Answer the following question.
Why photodiodes are required to operate in reverse bias? Explain.
Diffusion in a p-n junction is due to ______.
A – pn junction has a depletion layer of thickness .of the order of
When we apply reverse biased to a junction diode, it
The nature of binding for a crystal with alternate and evenly spaced positive and negatively ions is
In a semiconductor diode, the barrier potential offers opposition to only
Avalanche breakdown is due to ______.
In the circuit shown in figure, if the diode forward voltage drop is 0.3 V, the voltage difference between A and B is ______.

The breakdown in a reverse biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to ______.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large.
- strong electric field in a depletion region if the doping concentration is small.
- strong electric field in the depletion region if the doping concentration is large.
Can the potential barrier across a p-n junction be measured by simply connecting a voltmeter across the junction?
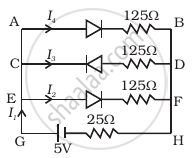
If each diode in figure has a forward bias resistance of 25 Ω and infinite resistance in reverse bias, what will be the values of the current I1, I2, I3 and I4?
Draw V-I characteristics of a p-n Junction diode.
Differentiate between the threshold voltage and the breakdown voltage for a diode.
Describe briefly the following term:
minority carrier injection in forward biasing.
