Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The given figure shows a rectangle ABDC and a parallelogram ABEF; drawn on opposite sides of AB.
Prove that:
(i) Quadrilateral CDEF is a parallelogram;
(ii) Area of the quad. CDEF
= Area of rect. ABDC + Area of // gm. ABEF.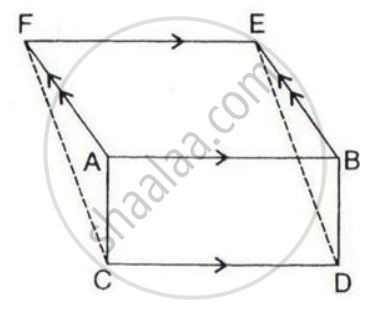
उत्तर
After drawing the opposite sides of AB, we get
Since from the figure, we get CD//FE, therefore, FC must parallel to DE. Therefore it is proved that the quadrilateral CDEF is a parallelogram.
The area of the parallelogram on the same base and between the same parallel lines is always equal and the area of the parallelogram is equal to the area of a rectangle on the same base and of the same altitude i.e, between the same parallel lines.
So Area of CDEF= Area of ABDC + Area of ABEF
Hence Proved
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the following, AC // PS // QR and PQ // DB // SR.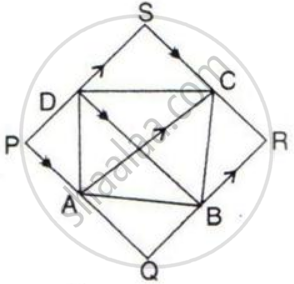
Prove that: Area of quadrilateral PQRS = 2 x Area of the quad. ABCD.
In the following figure, CE is drawn parallel to diagonals DB of the quadrilateral ABCD which meets AB produced at point E.
Prove that ΔADE and quadrilateral ABCD are equal in area.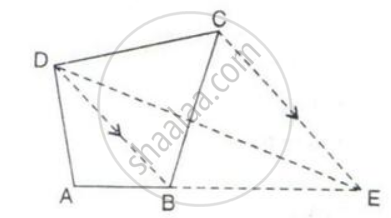
In the figure given alongside, squares ABDE and AFGC are drawn on the side AB and the hypotenuse AC of the right triangle ABC.
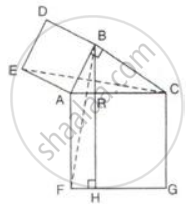
If BH is perpendicular to FG
prove that:
- ΔEAC ≅ ΔBAF
- Area of the square ABDE
- Area of the rectangle ARHF.
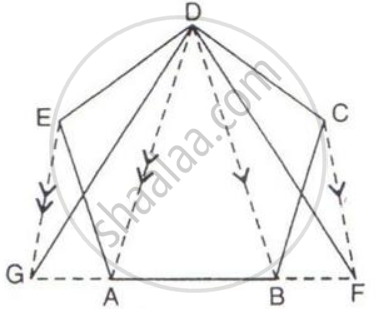
The given figure shows a pentagon ABCDE. EG drawn parallel to DA meets BA produced at G and CF draw parallel to DB meets AB produced at F.
Prove that the area of pentagon ABCDE is equal to the area of triangle GDF.
ABCD is a parallelogram in which BC is produced to E such that CE = BC and AE intersects CD at F.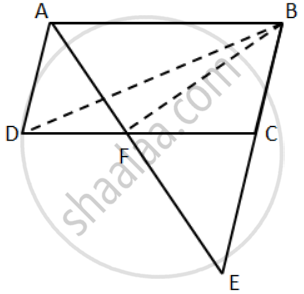
If ar.(∆DFB) = 30 cm2; find the area of parallelogram.
In the given figure, the diagonals AC and BD intersect at point O. If OB = OD and AB//DC,
show that:
(i) Area (Δ DOC) = Area (Δ AOB).
(ii) Area (Δ DCB) = Area (Δ ACB).
(iii) ABCD is a parallelogram.
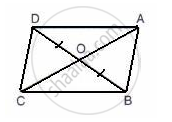
E, F, G, and H are the midpoints of the sides of a parallelogram ABCD.
Show that the area of quadrilateral EFGH is half of the area of parallelogram ABCD.
In the following figure, BD is parallel to CA, E is mid-point of CA and BD = `1/2`CA
Prove that: ar. ( ΔABC ) = 2 x ar.( ΔDBC )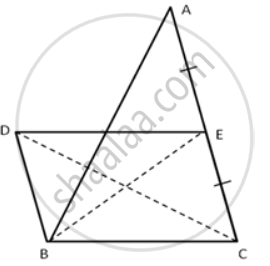
In parallelogram ABCD, E is a point in AB and DE meets diagonal AC at point F. If DF: FE = 5:3 and area of ΔADF is 60 cm2; find
(i) area of ΔADE.
(ii) if AE: EB = 4:5, find the area of ΔADB.
(iii) also, find the area of parallelogram ABCD.
In parallelogram ABCD, P is the mid-point of AB. CP and BD intersect each other at point O. If the area of ΔPOB = 40 cm2, and OP: OC = 1:2, find:
(i) Areas of ΔBOC and ΔPBC
(ii) Areas of ΔABC and parallelogram ABCD.
