Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The heights of 50 girls of Class X of a school are recorded as follows:
| Height (in cm) | 135 - 140 | 140 – 145 | 145 – 150 | 150 – 155 | 155 – 160 | 160 – 165 |
| No of Students | 5 | 8 | 9 | 12 | 14 | 2 |
Draw a ‘more than type’ ogive for the above data.
उत्तर
The frequency distribution table of more than type is as follows:
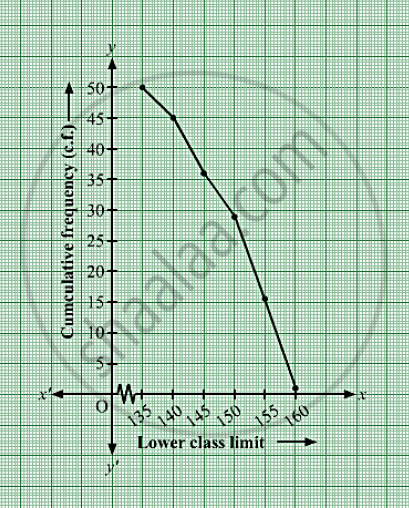
| Height (in cm) (lower class limit | Cumulative frequency (cf) |
| More than 135 | 5 + 45 = 50 |
| More than 140 | 8 + 37 = 45 |
| More than 145 | 9 + 28 = 37 |
| More than 150 | 12 + 16 = 28 |
| More than 155 | 14 + 2 = 16 |
| More than 160 | 2 |
Taking lower class limits of on x-axis and their respective cumulative frequencies on y-axis,its ogive can be drawn as follows:
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The table given below shows the weekly expenditures on food of some households in a locality
| Weekly expenditure (in Rs) | Number of house holds |
| 100 – 200 | 5 |
| 200- 300 | 6 |
| 300 – 400 | 11 |
| 400 – 500 | 13 |
| 500 – 600 | 5 |
| 600 – 700 | 4 |
| 700 – 800 | 3 |
| 800 – 900 | 2 |
Draw a ‘less than type ogive’ and a ‘more than type ogive’ for this distribution.
What is the lower limit of the modal class of the following frequency distribution?
| Age (in years) | 0 - 10 | 10- 20 | 20 -30 | 30 – 40 | 40 –50 | 50 – 60 |
| Number of patients | 16 | 13 | 6 | 11 | 27 | 18 |
The following are the ages of 300 patients getting medical treatment in a hospital on a particular day:
| Age (in years) | 10 – 20 | 20 – 30 | 30 – 40 | 40 – 50 | 50 – 60 | 60 -70 |
| Number of patients | 6 | 42 | 55 | 70 | 53 | 20 |
Form a ‘less than type’ cumulative frequency distribution.
The following frequency distribution gives the monthly consumption of electricity of 64 consumers of locality.
| Monthly consumption (in units) | 65 – 85 | 85 – 105 | 105 – 125 | 125 – 145 | 145 – 165 | 165 – 185 |
| Number of consumers | 4 | 5 | 13 | 20 | 14 | 8 |
Form a ‘ more than type’ cumulative frequency distribution.
If the median of the following frequency distribution is 32.5. Find the values of f1 and f2.
Change the following distribution to a 'more than type' distribution. Hence draw the 'more than type' ogive for this distribution.
| Class interval: | 20−30 | 30−40 | 40−50 | 50−60 | 60−70 | 70−80 | 80−90 |
| Frequency: | 10 | 8 | 12 | 24 | 6 | 25 | 15 |
Look at the following table below.
| Class interval | Classmark |
| 0 - 5 | A |
| 5 - 10 | B |
| 10 - 15 | 12.5 |
| 15 - 20 | 17.5 |
The value of A and B respectively are?
If the sum of all the frequencies is 24, then the value of z is:
| Variable (x) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Frequency | z | 5 | 6 | 1 | 2 |
The following is the distribution of weights (in kg) of 40 persons:
| Weight (in kg) | 40 – 45 | 45 – 50 | 50 – 55 | 55 – 60 | 60 – 65 | 65 – 70 | 70 – 75 | 75 – 80 |
| Number of persons | 4 | 4 | 13 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 1 |
Construct a cumulative frequency distribution (of the less than type) table for the data above.
The following table shows the cumulative frequency distribution of marks of 800 students in an examination:
| Marks | Number of students |
| Below 10 | 10 |
| Below 20 | 50 |
| Below 30 | 130 |
| Below 40 | 270 |
| Below 50 | 440 |
| Below 60 | 570 |
| Below 70 | 670 |
| Below 80 | 740 |
| Below 90 | 780 |
| Below 100 | 800 |
Construct a frequency distribution table for the data above.
