Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The intensity of sound from a point source is 1.0 × 10−8 W m−2 at a distance of 5.0 m from the source. What will be the intensity at a distance of 25 m from the source?
उत्तर
Given:
The intensity I1 is 1.0 × 10−8 Wm−2,
when the distance of the point source \[r_1\]is 5 m.
Let I2 be the intensity of the point source at a distance \[r_2\]= 25 m.
As we know,
\[I \propto \left( \frac{1}{r^2} \right) . \]
\[\text { So }, \]
\[\frac{I_1}{I_2} = \frac{{r_2}^2}{{r_1}^1}\]
\[ \Rightarrow I_2 = \frac{I_1 {r_1}^2}{{r_2}^2}\]
On substituting the respective values, we get:
\[ I_2 = \frac{1 . 0 \times {10}^{- 8} \times 25}{625}\] \[ = 4 . 0 \times {10}^{- 10} \text { W/ m }^2\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A wave is represented by an equation \[y = c_1 \sin \left( c_2 x + c_3 t \right)\] In which direction is the wave going? Assume that \[c_1 , c_2\] \[c_3\] are all positive.
Two loudspeakers are arranged facing each other at some distance. Will a person standing behind one of the loudspeakers clearly hear the sound of the other loudspeaker or the clarity will be seriously damaged because of the 'collision' of the two sounds in between?
The bulk modulus and the density of water are greater than those of air. With this much of information, we can say that velocity of sound in air
A tuning fork sends sound waves in air. If the temperature of the air increases, which of the following parameters will change?
The fundamental frequency of a vibrating organ pipe is 200 Hz.
(a) The first overtone is 400 Hz.
(b) The first overtone may be 400 Hz.
(c) The first overtone may be 600 Hz.
(d) 600 Hz is an overtone.
A man stands before a large wall at a distance of 50.0 m and claps his hands at regular intervals. Initially, the interval is large. He gradually reduces the interval and fixes it at a value when the echo of a clap merges every 3 seconds, find the velocity of sound in air.
The absolute temperature of air in a region linearly increases from T1 to T2 in a space of width d. Find the time taken by a sound wave to go through the region in terms of T1, T2, d and the speed v of sound at 273 K. Evaluate this time for T1 = 280 K, T2 = 310 K, d = 33 m and v = 330 m s−1.
Sound with intensity larger than 120 dB appears pain full to a person. A small speaker delivers 2.0 W of audio output. How close can the person get to the speaker without hurting his ears?
The noise level in a classroom in absence of the teacher is 50 dB when 50 students are present. Assuming that on the average each student output same sound energy per second, what will be the noise level if the number of students is increased to 100?
A uniform horizontal rod of length 40 cm and mass 1⋅2 kg is supported by two identical wires as shown in figure. Where should a mass of 4⋅8 kg be placed on the rod so that the same tuning fork may excite the wire on left into its fundamental vibrations and that on right into its first overtone? Take g = 10 m s−2.
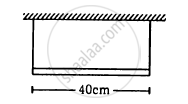
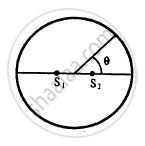
Figure shown two coherent sources S1 and S2 which emit sound of wavelength λ in phase. The separation between the sources is 3λ. A circular wire of large radius is placed in such way that S1,S2 is at the centre of the wire. Find the angular positions θ on the wire for which constructive interference takes place.
The separation between a node and the next antinode in a vibrating air column is 25 cm. If the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the frequency of vibration of the air column.
A source of sound with adjustable frequency produces 2 beats per second with a tuning fork when its frequency is either 476 Hz of 480 Hz. What is the frequency of the tuning fork?
A cylindrical tube, open at both ends, has a fundamental frequency v. The tube is dipped vertically in water so that half of its length is inside the water. The new fundamental frequency is
A piano wire A vibrates at a fundamental frequency of 600 Hz. A second identical wire Bproduces 6 beats per second with it when the tension in A is slightly increased. Find the the ratio of the tension in A to the tension in B.
A train running at 108 km h−1 towards east whistles at a dominant frequency of 500 Hz. Speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. What frequency will a passenger sitting near the open window hear? (b) What frequency will a person standing near the track hear whom the train has just passed? (c) A wind starts blowing towards east at a speed of 36 km h−1. Calculate the frequencies heard by the passenger in the train and by the person standing near the track.
A person standing on a road sends a sound signal to the driver of a car going away from him at a speed of 72 km h−1. The signal travelling at 330 m s−1 in air and having a frequency of 1600 Hz gets reflected from the body of the car and returns. Find the frequency of the reflected signal as heard by the person.
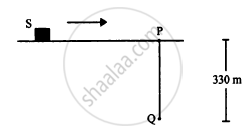
Figure shows a source of sound moving along X-axis at a speed of 22 m s−1continuously emitting a sound of frequency 2.0 kHz which travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener Q stands on the Y-axis at a distance of 330 m from the origin. At t = 0, the sources crosses the origin P. (a) When does the sound emitted from the source at P reach the listener Q? (b) What will be the frequency heard by the listener at this instant? (c) Where will the source be at this instant?
In the wave equation
`y = 0.5sin (2pi)/lambda(400t - x)m`
the velocity of the wave will be ______.
