Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two loudspeakers are arranged facing each other at some distance. Will a person standing behind one of the loudspeakers clearly hear the sound of the other loudspeaker or the clarity will be seriously damaged because of the 'collision' of the two sounds in between?
उत्तर
It depends on the position of the speakers. The placement decides whether the interference so formed is constructive or destructive.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A wave is represented by an equation \[y = c_1 \sin \left( c_2 x + c_3 t \right)\] In which direction is the wave going? Assume that \[c_1 , c_2\] \[c_3\] are all positive.
If you are walking on the moon, can you hear the sound of stones cracking behind you? Can you hear the sound of your own footsteps?
Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross section by the first wave be P1 and that by the second wave be P2. Then
The fundamental frequency of a vibrating organ pipe is 200 Hz.
(a) The first overtone is 400 Hz.
(b) The first overtone may be 400 Hz.
(c) The first overtone may be 600 Hz.
(d) 600 Hz is an overtone.
A steel tube of length 1.00 m is struck at one end. A person with his ear closed to the other end hears the sound of the blow twice, one travelling through the body of the tube and the other through the air in the tube. Find the time gap between the two hearings. Use the table in the text for speeds of sound in various substances.
The absolute temperature of air in a region linearly increases from T1 to T2 in a space of width d. Find the time taken by a sound wave to go through the region in terms of T1, T2, d and the speed v of sound at 273 K. Evaluate this time for T1 = 280 K, T2 = 310 K, d = 33 m and v = 330 m s−1.
If the intensity of sound is doubled, by how many decibels does the sound level increase?
A string of length L fixed at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode at a frequency ν and a maximum amplitude A. (a)
- Find the wavelength and the wave number k.
- Take the origin at one end of the string and the X-axis along the string. Take the Y-axis along the direction of the displacement. Take t = 0 at the instant when the middle point of the string passes through its mean position and is going towards the positive y-direction. Write the equation describing the standing wave.
Two coherent narrow slits emitting sound of wavelength λ in the same phase are placed parallel to each other at a small separation of 2λ. The sound is detected by moving a detector on the screen ∑ at a distance D(>>λ) from the slit S1 as shown in figure. Find the distance x such that the intensity at P is equal to the intensity at O.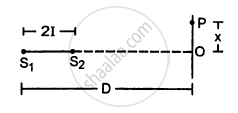
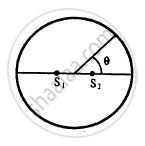
Figure shown two coherent sources S1 and S2 which emit sound of wavelength λ in phase. The separation between the sources is 3λ. A circular wire of large radius is placed in such way that S1,S2 is at the centre of the wire. Find the angular positions θ on the wire for which constructive interference takes place.
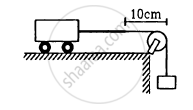
A heavy string is tied at one end to a movable support and to a light thread at the other end as shown in following figure. The thread goes over a fixed pulley and supports a weight to produce a tension. The lowest frequency with which the heavy string resonates is 120 Hz. If the movable support is pushed to the right by 10 cm so that the joint is placed on the pulley, what will be the minimum frequency at which the heavy string can resonate?
In a standing wave pattern in a vibrating air column, nodes are formed at a distance of 4.0 cm. If the speed of sound in air is 328 m s−1, what is the frequency of the source?
A cylindrical tube, open at both ends, has a fundamental frequency v. The tube is dipped vertically in water so that half of its length is inside the water. The new fundamental frequency is
A piano wire A vibrates at a fundamental frequency of 600 Hz. A second identical wire Bproduces 6 beats per second with it when the tension in A is slightly increased. Find the the ratio of the tension in A to the tension in B.
Two electric trains run at the same speed of 72 km h−1 along the same track and in the same direction with separation of 2.4 km between them. The two trains simultaneously sound brief whistles. A person is situated at a perpendicular distance of 500 m from the track and is equidistant from the two trains at the instant of the whistling. If both the whistles were at 500 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the frequencies heard by the person.
A small source of sound oscillates in simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 17 cm. A detector is placed along the line of motion of the source. The source emits a sound of frequency 800 Hz which travels at a speed of 340 m s−1. If the width of the frequency band detected by the detector is 8 Hz, find the time period of the source.
A boy riding on his bike is going towards east at a speed of 4√2 m s−1. At a certain point he produces a sound pulse of frequency 1650 Hz that travels in air at a speed of 334 m s−1. A second boy stands on the ground 45° south of east from his. Find the frequency of the pulse as received by the second boy.
A boy riding on a bicycle going at 12 km h−1 towards a vertical wall whistles at his dog on the ground. If the frequency of the whistle is 1600 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 330 m s−1, find (a) the frequency of the whistle as received by the wall (b) the frequency of the reflected whistle as received by the boy.
A small source of sound S of frequency 500 Hz is attached to the end of a light string and is whirled in a vertical circle of radius 1.6 m. The string just remains tight when the source is at the highest point. (a) An observer is located in the same vertical plane at a large distance and at the same height as the centre of the circle. The speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1 and g = 10 m s−2. Find the maximum frequency heard by the observer. (b) An observer is situated at a large distance vertically above the centre of the circle. Find the frequency heard by the observer corresponding to the sound emitted by the source when it is at the same height as the centre.