Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A boy riding on a bicycle going at 12 km h−1 towards a vertical wall whistles at his dog on the ground. If the frequency of the whistle is 1600 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 330 m s−1, find (a) the frequency of the whistle as received by the wall (b) the frequency of the reflected whistle as received by the boy.
उत्तर
Given:
Velocity of sound in air v = 330 ms−1
(a) Frequency of whistle \[n_0\]=1600 Hz
Velocity of source vs = 12 km/h =\[12 \times \frac{5}{18} = \frac{10}{3} {\text { ms }}^{- 1}\]
Velocity of an observer \[v_0\] = 0 ms−1
Frequency of whistle received by wall n =?Frequency of sound received by the observer is given by :
\[n = \frac{v + v_0}{v - v_s} \times n_0\]
On substituting the respective values in the above formula, we get :
\[n = \frac{330 + 0}{330 - \frac{10}{3}} \times 1600 = 1616 \text{ Hz }\]
(b) Here,
Velocity of observer \[v_0\] \[\frac{10}{3} {\text { ms }}^{- 1}\]
Velocity of source vs = 0
Frequency of source \[n_0\]= 1616 Hz
Frequency of sound heard by observer is
\[n = \frac{v + v_0}{v + v_s} \times n_0 \]
On substituting the respective values in the above formula, we get :
\[= \frac{330 + \frac{10}{3}}{330 + 0} \times 1616 = 1632 \text{ Hz }\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the smallest positive phase constant which is equivalent to 7⋅5 π?
When we clap our hands, the sound produced is best described by Here p denotes the change in pressure from the equilibrium value.
Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross section by the first wave be P1 and that by the second wave be P2. Then
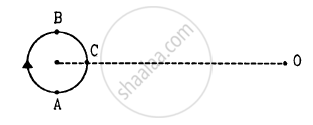
A small source of sounds moves on a circle as shown in figure and an observer is sitting at O. Let \[v_1, v_2, v_3\] be the frequencies heard when the source is at A, B and C respectively.
A steel tube of length 1.00 m is struck at one end. A person with his ear closed to the other end hears the sound of the blow twice, one travelling through the body of the tube and the other through the air in the tube. Find the time gap between the two hearings. Use the table in the text for speeds of sound in various substances.
A man stands before a large wall at a distance of 50.0 m and claps his hands at regular intervals. Initially, the interval is large. He gradually reduces the interval and fixes it at a value when the echo of a clap merges every 3 seconds, find the velocity of sound in air.
The equation of a travelling sound wave is y = 6.0 sin (600 t − 1.8 x) where y is measured in 10−5 m, t in second and x in metre. (a) Find the ratio of the displacement amplitude of the particles to the wavelength of the wave. (b) Find the ratio of the velocity amplitude of the particles to the wave speed.
A sound wave frequency 100 Hz is travelling in air. The speed of sound in air is 350 m s−1. (a) By how much is the phase changed at a given point in 2.5 ms? (b) What is the phase difference at a given instant between two points separated by a distance of 10.0 cm along the direction of propagation?
Calculate the bulk modulus of air from the following data about a sound wave of wavelength 35 cm travelling in air. The pressure at a point varies between (1.0 × 105 ± 14) Pa and the particles of the air vibrate in simple harmonic motion of amplitude 5.5 × 10−6 m.
The intensity of sound from a point source is 1.0 × 10−8 W m−2 at a distance of 5.0 m from the source. What will be the intensity at a distance of 25 m from the source?
If the intensity of sound is doubled, by how many decibels does the sound level increase?
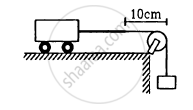
A heavy string is tied at one end to a movable support and to a light thread at the other end as shown in following figure. The thread goes over a fixed pulley and supports a weight to produce a tension. The lowest frequency with which the heavy string resonates is 120 Hz. If the movable support is pushed to the right by 10 cm so that the joint is placed on the pulley, what will be the minimum frequency at which the heavy string can resonate?
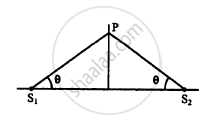
Two sources of sound S1 and S2 vibrate at same frequency and are in phase. The intensity of sound detected at a point P as shown in the figure is I0. (a) If θ equals 45°, what will be the intensity of sound detected at this point if one of the sources is switched off? (b) What will be the answer of the previous part if θ = 60°?
A source of sound with adjustable frequency produces 2 beats per second with a tuning fork when its frequency is either 476 Hz of 480 Hz. What is the frequency of the tuning fork?
A piano wire A vibrates at a fundamental frequency of 600 Hz. A second identical wire Bproduces 6 beats per second with it when the tension in A is slightly increased. Find the the ratio of the tension in A to the tension in B.
A sound source, fixed at the origin, is continuously emitting sound at a frequency of 660 Hz. The sound travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener is moving along the lien x= 336 m at a constant speed of 26 m s−1. Find the frequency of the sound as observed by the listener when he is (a) at y = − 140 m, (b) at y = 0 and (c) at y = 140 m.
A person standing on a road sends a sound signal to the driver of a car going away from him at a speed of 72 km h−1. The signal travelling at 330 m s−1 in air and having a frequency of 1600 Hz gets reflected from the body of the car and returns. Find the frequency of the reflected signal as heard by the person.
For the propagation of longitudinal waves, the medium must have
- elasticity
- mass
- inertia
- force of cohesion
The speed of a wave in a string is 20 m/s and the frequency is 50 Hz. The phase difference between two points on the string 10 cm apart will be ______.
