Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The measure of angles of a hexagon are x°, (x − 5)°, (x − 5)°, (2x − 5)°, (2x − 5)°, (2x + 20)°. Find the value of x.
उत्तर
\[\text{ Since the sum of all the angles of a hexagon is } 720° , \text{ we get } : \]
\[x° + \left( x - 5 \right)° + \left( x - 5 \right)° + \left( 2x - 5 \right)° + \left( 2x - 5 \right)° + \left( 2x + 20 \right)° = 720°\]
\[ \Rightarrow x° + x° - 5° + x°- 5°+ 2x - 5°+ 2x - 5°+ 2x + 20°= 720° \]
\[ \Rightarrow 9x - 20° + 20° = 720° \]
\[ \Rightarrow 9x = 720° \]
\[ \therefore x = 80\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The number of pairs of adjacent angles of a quadrilateral is .......
In Fig. 16.19, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
How many pairs of adjacent angles are there?
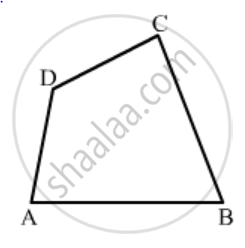
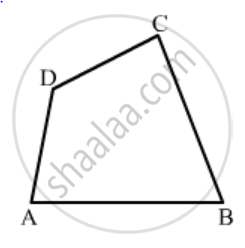
In Fig. 16.19, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
How many pairs of opposite angles are there?
A quadrilateral has all its four angles of the same measure. What is the measure of each?
Given : In quadrilateral ABCD ; ∠C = 64°, ∠D = ∠C – 8° ; ∠A = 5(a+2)° and ∠B = 2(2a+7)°.
Calculate ∠A.
The angles A, B, C and D of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 2 : 3 : 2 : 3. Show this quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
One diagonal of a rectangle is 18 cm. What is the length of its other diagonal?
D and E are the mid-points of the sides AB and AC respectively of ∆ABC. DE is produced to F. To prove that CF is equal and parallel to DA, we need an additional information which is ______.
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
OP ⊥ AB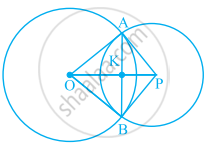
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral KLMN. State two pairs of adjacent angles.
