Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given : In quadrilateral ABCD ; ∠C = 64°, ∠D = ∠C – 8° ; ∠A = 5(a+2)° and ∠B = 2(2a+7)°.
Calculate ∠A.
उत्तर
∵ ∠C = 64° (Given)
∴ ∠D = ∠C – 8° = 64°- 8° = 56°
∠A = 5(a+2)°
∠B = 2(2a+7)°
Now ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
5(a+2)° + 2(2a+7)° + 64° + 56° = 360°
5a + 10 + 4a + 14° + 64° + 56° = 360°
9a + 144° = 360°
9a = 360° – 144°
9a = 216°
a = 24°
∴ ∠A = 5 (a + 2) = 5(24+2) = 130°
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the following term Convex Quadrilateral .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Angles .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Adjacent angles .
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has .... diagonals.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
In a quadrilateral the point of intersection of the diagonals lies in .... of the quadrilateral.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A point is in the interior of a convex quadrilateral, if it is in the ..... of its two opposite angles.
In Fig. 16.19, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
Name a pair of opposite sides.
The angles of a quadrilateral are 110°, 72°, 55° and x°. Find the value of x.
Three angles of a quadrilateral are equal. Fourth angle is of measure 150°. What is the measure of equal angles.
The four angles of a quadrilateral are as 3 : 5 : 7 : 9. Find the angles.
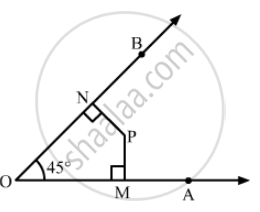
In Fig. 16.20, find the measure of ∠MPN.
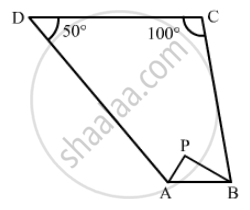
In Fig. 16.21, the bisectors of ∠A and ∠B meet at a point P. If ∠C = 100° and ∠D = 50°, find the measure of ∠APB.
The measure of angles of a hexagon are x°, (x − 5)°, (x − 5)°, (2x − 5)°, (2x − 5)°, (2x + 20)°. Find the value of x.
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If one pair of opposite sides are equal and parallel, then the figure is ........................
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If opposite angles of a quadrilateral are equal, then it is necessarily a ....................
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
f consecutive sides of a parallelogram are equal, then it is necessarily a ..................
If ABCD is a rectangle with ∠BAC = 32°, find the measure of ∠DBC.
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
The opposite sides of a quadrilateral have
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 68° and 76°. If the other two angles are in the ratio 5 : 7; find the measure of each of them.
From the following figure find;
- x
- ∠ABC
- ∠ACD
In a parallelogram ABCD, its diagonals AC and BD intersect each other at point O.
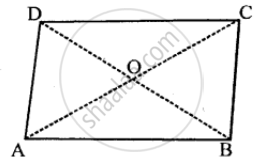
If AC = 12 cm and BD = 9 cm ; find; lengths of OA and OD.
Find the angles of a pentagon which are in the ratio 4: 4: 6: 7: 6.
The angles of a pentagon are x°, (x - 10)°, (x + 20)°, (2x - 44)° and (2x - 70)°. Find the angles.
A diagonal of a rectangle is inclined to one side of the rectangle at 25º. The acute angle between the diagonals is ______.
Construct a quadrilateral NEWS in which NE = 7 cm, EW = 6 cm, ∠N = 60°, ∠E = 110° and ∠S = 85°.
In the given figure.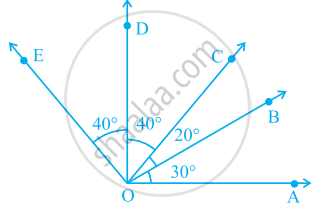
∠AOD is a/an ____ angle
In the given figure.
∠COA is a/an ______ angle
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
AC ⊥ BD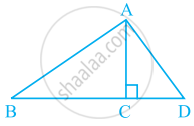
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
AE ⊥ CE
