Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Given : In quadrilateral ABCD ; ∠C = 64°, ∠D = ∠C – 8° ; ∠A = 5(a+2)° and ∠B = 2(2a+7)°.
Calculate ∠A.
Solution
∵ ∠C = 64° (Given)
∴ ∠D = ∠C – 8° = 64°- 8° = 56°
∠A = 5(a+2)°
∠B = 2(2a+7)°
Now ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
5(a+2)° + 2(2a+7)° + 64° + 56° = 360°
5a + 10 + 4a + 14° + 64° + 56° = 360°
9a + 144° = 360°
9a = 360° – 144°
9a = 216°
a = 24°
∴ ∠A = 5 (a + 2) = 5(24+2) = 130°
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define the following term Quadrilateral .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Adjacent sides .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Opposite sides .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Interior .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Exterior .
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has ...... angles.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has ..... vertices, no three of which are .....
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has .... diagonals.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The number of pairs of opposite angles of a quadrilateral is .......
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The sum of the angles of a quiadrilateral is .... right angles.
In Fig. 16.19, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
Name a pair of opposite sides.
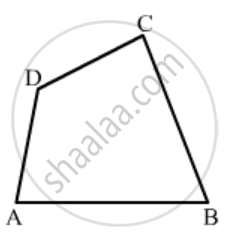
In Fig. 16.19, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
How many pairs of opposite sides are there?
A quadrilateral has all its four angles of the same measure. What is the measure of each?
If the sum of the two angles of a quadrilateral is 180°. What is the sum of the remaining two angles?
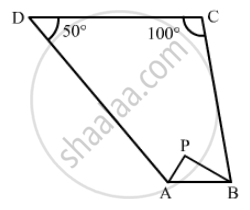
In Fig. 16.21, the bisectors of ∠A and ∠B meet at a point P. If ∠C = 100° and ∠D = 50°, find the measure of ∠APB.
The angles A, B, C and D of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 2 : 3 : 2 : 3. Show this quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
Write two conditions that will make the adjoining figure a square.
Observe the figure below and find out their name.
Observe the figure below and find out their name.
The angles of a hexagon are (2x + 5)°, (3x - 5)°, (x + 40)°, (2x + 20)°, (2x + 25)° and (2x + 35)°. Find the value of x.
In the quadrilateral ABCD, AB = BC and AD = DC Measure of ∠BCD is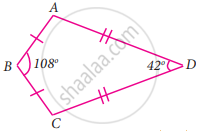
In the figure, PQRS and PTVS are two cyclic quadrilaterals, If ∠QRS = 100°, then ∠TVS =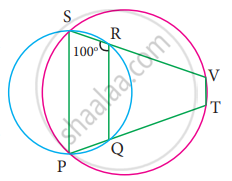
A quadrilateral can be drawn when all the four angles and one side is given.
In figure, if point A is shifted to point B along the ray PX such that PB = 2PA, then the measure of ∠BPY is ______.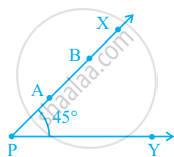
A pair of opposite sides of a trapezium are ______.
In the given figure.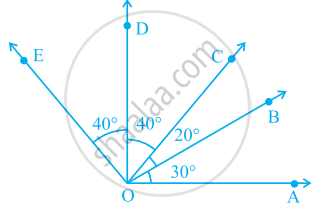
∠COA is a/an ______ angle
What conclusion can be drawn from part of given figure, if DB is the bisector of ∠ADC?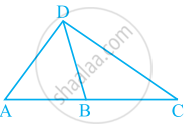
What conclusion can be drawn from part of given figure, if BD bisects ∠ABC?
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral KLMN. State two pairs of opposite sides.
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral KLMN. State two pairs of opposite angles.
