Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
From the following figure find;
- x
- ∠ABC
- ∠ACD
Solution
(i) In Quadrilateral ABCD,
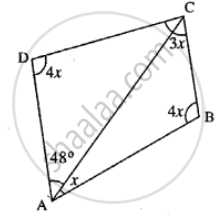
x + 4x + 3x + 4x + 48° = 360°
12x = 360° – 48°
12x = 312
x = `312/12` = 26°
(ii) ∠ABC = 4x
4 × 26 = 104°
(iii) ∠ACD = 180° − 4x − 48°
= 180° − 4 × 26° − 48°
= 180° − 104° − 48°
= 180° − 152° = 28°
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Adjacent sides .
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The number of pairs of adjacent angles of a quadrilateral is .......
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The number of pairs of opposite angles of a quadrilateral is .......
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The measure of each angle of a convex quadrilateral is ..... 180°.
Two angles of a quadrilateral are of measure 65° and the other two angles are equal. What is the measure of each of these two angles?
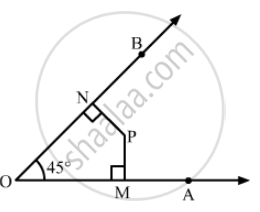
In Fig. 16.20, find the measure of ∠MPN.
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If in a quadrilateral only one pair of opposite sides are parallel, the quadrilateral is ................
Which of the following quadrilateral is not a rhombus?
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 68° and 76°. If the other two angles are in the ratio 5 : 7; find the measure of each of them.
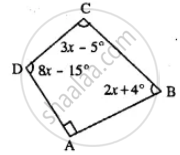
Use the information given in the following figure to find :
(i) x
(ii) ∠B and ∠C
ABCDE is a regular pentagon. The bisector of angle A of the pentagon meets the side CD in point M. Show that ∠AMC = 90°.
In a parallelogram ABCD, its diagonals AC and BD intersect each other at point O.
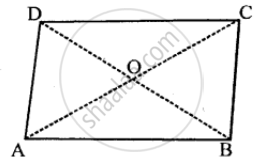
If AC = 12 cm and BD = 9 cm ; find; lengths of OA and OD.
One diagonal of a rectangle is 18 cm. What is the length of its other diagonal?
Observe the figure below and find out their name.
The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 2 : 4 : 5 : 7. Find all the angles
If bisectors of ∠A and ∠B of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at P, of ∠B and ∠C at Q, of ∠C and ∠D at R and of ∠D and ∠A at S, then PQRS is a ______.
If APB and CQD are two parallel lines, then the bisectors of the angles APQ, BPQ, CQP and PQD form ______.
In quadrilateral HOPE, the pairs of opposite sides are ______.
In quadrilateral ROPE, the pairs of adjacent angles are ______.
The diagonals of the quadrilateral DEFG are ______ and ______.
In figure, if point A is shifted to point B along the ray PX such that PB = 2PA, then the measure of ∠BPY is ______.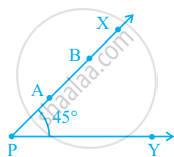
If the sum of two angles is equal to an obtuse angle, then which of the following is not possible?
In the given figure.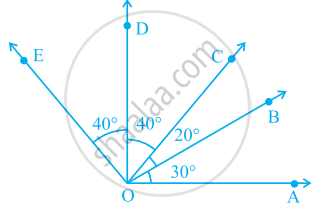
∠COA is a/an ______ angle
The number of common points in the two angles marked in figure is ______.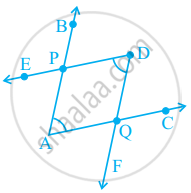
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
BA ⊥BD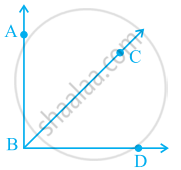
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
AC ⊥ CD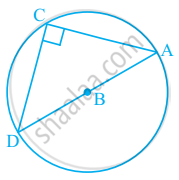
What conclusion can be drawn from part of given figure, if DB is the bisector of ∠ADC?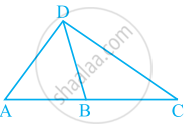
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral PQRS. Draw its diagonals. Name them. Is the meeting point of the diagonals in the interior or exterior of the quadrilateral?