Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
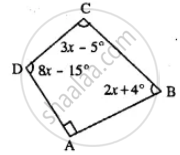
Use the information given in the following figure to find :
(i) x
(ii) ∠B and ∠C
Solution
∵ ∠A = 90° (Given)
∠B = (2x + 4°)
∠C = (3x - 5°)
∠D = (8x - 15°)
∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
90° + (2x + 4°) + (3x - 5°) + (8x - 15°) = 360°
90° + 2x + 4° + 3x - 5° + 8x - 15° = 360°
⇒ 74° + 13x = 360°
⇒ 13x = 360° - 74°
⇒ 13x = 286°
⇒ `x = 286/13`
⇒ x = 22°
∵ ∠B = 2x 4 = 2 × 22° + 4 = 48°
∠C = 3x - 5 = 3 × 22° - 5 = 61°
Hence (i) 22° (ii) ∠B = 48°, ∠C = 61°
RELATED QUESTIONS
Given here are some figures:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Classify each of them on the basis of the following:
- Simple curve
- Simple closed curve
- Polygon
- Convex polygon
- Concave polygon
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Interior .
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has ..... vertices, no three of which are .....
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has .... diagonals.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The number of pairs of opposite angles of a quadrilateral is .......
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The sum of the angles of a quiadrilateral is .... right angles.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral is convex if, for each side, the remaining ______ lie on the same side of the line containing the side.
In Fig. 16.19, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
Name a pair of adjacent angles.
The angles of a quadrilateral are 110°, 72°, 55° and x°. Find the value of x.
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
f consecutive sides of a parallelogram are equal, then it is necessarily a ..................
If the bisectors of two adjacent angles A and B of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect at a point O such that ∠C + ∠D = k ∠AOB, then find the value of k.
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 89° and 113°. If the other two angles are equal; find the equal angles.
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 68° and 76°. If the other two angles are in the ratio 5 : 7; find the measure of each of them.
In quadrilateral ABCD, side AB is parallel to side DC. If ∠A : ∠D = 1 : 2 and ∠C : ∠B = 4 : 5
(i) Calculate each angle of the quadrilateral.
(ii) Assign a special name to quadrilateral ABCD
In an isosceles trapezium one pair of opposite sides are _____ to each Other and the other pair of opposite sides are _____ to each other.
Two opposite angles of a parallelogram are 100° each. Find each of the other two opposite angles.
In a parallelogram ABCD, its diagonals AC and BD intersect each other at point O.
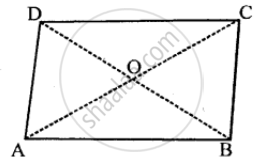
If AC = 12 cm and BD = 9 cm ; find; lengths of OA and OD.
Write, giving reason, the name of the figure drawn alongside. Under what condition will this figure be a square.
Observe the figure below and find out their name.
If one angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is 75°, then the opposite angle is
A diagonal of a rectangle is inclined to one side of the rectangle at 25º. The acute angle between the diagonals is ______.
D and E are the mid-points of the sides AB and AC respectively of ∆ABC. DE is produced to F. To prove that CF is equal and parallel to DA, we need an additional information which is ______.
A quadrilateral can have all four angles as obtuse.
Construct a quadrilateral NEWS in which NE = 7 cm, EW = 6 cm, ∠N = 60°, ∠E = 110° and ∠S = 85°.
If the sum of two angles is greater than 180°, then which of the following is not possible for the two angles?
In the given figure.
∠AOD is a/an ____ angle
The number of right angles in a straight angle is ______ and that in a complete angle is ______.
Can we have two obtuse angles whose sum is a complete angle? Why or why not?
