Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In an isosceles trapezium one pair of opposite sides are _____ to each Other and the other pair of opposite sides are _____ to each other.
Solution
In an isosceles trapezium one pair of opposite sides are parallel to each other and the other pair of opposite sides are equal to each other.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Exterior .
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has ....... sides.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has ...... angles.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A diagonal of a quadrilateral is a line segment that joins two ...... vertices of the quadrilateral.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, the angles A, B, C and D are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 4 : 5. Find the measure of each angle of the quadrilateral.
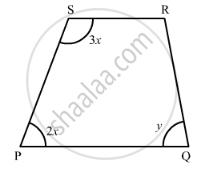
In the given figure, PQRS is an isosceles trapezium. Find x and y.
In the given figure, ABCD is a trapezium. Find the values of x and y.

Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If opposite angles of a quadrilateral are equal, then it is necessarily a ....................
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC. M and N are the mid-points of AD and the respectively. If AB = 12 cm, MN = 14 cm, then CD =
Two adjacent angles of a parallelogram are 70° and 110° respectively. Find the other two angles of it.
In parallelogram ABCD, its diagonals intersect at point O. If OA = 6 cm and OB = 7.5 cm, find the length of AC and BD.

One diagonal of a rectangle is 18 cm. What is the length of its other diagonal?
The three angles of a quadrilateral are 71°, 110°, 95°. Find its fourth angle.
Find the angles of a quadrilateral whose angles are in the ratio 1: 4: 5: 2.
In a pentagon ABCDE, AB || ED and ∠B = 140°, ∠C = 2x° and ∠D = 3x°. Find ∠C and ∠D
D and E are the mid-points of the sides AB and AC respectively of ∆ABC. DE is produced to F. To prove that CF is equal and parallel to DA, we need an additional information which is ______.
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AB || DC and AD = BC. Prove that ∠A = ∠B and ∠C = ∠D.
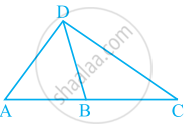
Number of angles less than 180° in figure is ______ and their names are ______.
What conclusion can be drawn from part of given figure, if DB is the bisector of ∠ADC?