Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Velocity of sound in air is 332 m s−1. Its velocity in vacuum will be
विकल्प
> 332 m s−1
= 332 m s−1
< 332 m s−1
meaningless.
उत्तर
meaningless
Sound wave is a mechanical wave; this means that it needs a medium to travel. Thus, its velocity in vacuum is meaningless.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
You have learnt that a travelling wave in one dimension is represented by a function y= f (x, t)where x and t must appear in the combination x – v t or x + v t, i.e. y = f (x ± v t). Is the converse true? Examine if the following functions for y can possibly represent a travelling wave:
(a) `(x – vt )^2`
(b) `log [(x + vt)/x_0]`
(c) `1/(x + vt)`
A bat emits an ultrasonic sound of frequency 1000 kHz in the air. If the sound meets a water surface, what is the wavelength of the transmitted sound? The speed of sound in air is 340 m s–1 and in water 1486 m s–1.
(i) For the wave on a string described in Exercise 15.11, do all the points on the string oscillate with the same (a) frequency, (b) phase, (c) amplitude? Explain your answers. (ii) What is the amplitude of a point 0.375 m away from one end?
A metre-long tube open at one end, with a movable piston at the other end, shows resonance with a fixed frequency source (a tuning fork of frequency 340 Hz) when the tube length is 25.5 cm or 79.3 cm. Estimate the speed of sound in air at the temperature of the experiment. The edge effects may be neglected.
A train, standing in a station-yard, blows a whistle of frequency 400 Hz in still air. The wind starts blowing in the direction from the yard to the station with at a speed of 10 m s–1. What are the frequency, wavelength, and speed of sound for an observer standing on the station’s platform? Is the situation exactly identical to the case when the air is still and the observer runs towards the yard at a speed of 10 m s–1? The speed of sound in still air can be taken as 340 m s–1.
A SONAR system fixed in a submarine operates at a frequency 40.0 kHz. An enemy submarine moves towards the SONAR with a speed of 360 km h–1. What is the frequency of sound reflected by the submarine? Take the speed of sound in water to be 1450 m s–1.
Earthquakes generate sound waves inside the earth. Unlike a gas, the earth can experience both transverse (S) and longitudinal (P) sound waves. Typically the speed of S wave is about 4.0 km s–1, and that of P wave is 8.0 km s–1. A seismograph records P and S waves from an earthquake. The first P wave arrives 4 min before the first S wave. Assuming the waves travel in straight line, at what distance does the earthquake occur?
A sine wave is travelling in a medium. A particular particle has zero displacement at a certain instant. The particle closest to it having zero displacement is at a distance
A wave pulse, travelling on a two-piece string, gets partially reflected and partially transmitted at the junction. The reflected wave is inverted in shape as compared to the incident one. If the incident wave has wavelength λ and the transmitted wave λ'
Two wave pulses travel in opposite directions on a string and approach each other. The shape of one pulse is inverted with respect to the other.
A wave propagates on a string in the positive x-direction at a velocity \[\nu\] \[t = t_0\] is given by \[g\left( x, t_0 \right) = A \sin \left( x/a \right)\]. Write the wave equation for a general time t.
Two waves, travelling in the same direction through the same region, have equal frequencies, wavelengths and amplitudes. If the amplitude of each wave is 4 mm and the phase difference between the waves is 90°, what is the resultant amplitude?
A 40 cm wire having a mass of 3⋅2 g is stretched between two fixed supports 40⋅05 cm apart. In its fundamental mode, the wire vibrates at 220 Hz. If the area of cross section of the wire is 1⋅0 mm2, find its Young modulus.
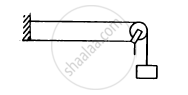
Following figure shows a string stretched by a block going over a pulley. The string vibrates in its tenth harmonic in unison with a particular tuning for. When a beaker containing water is brought under the block so that the block is completely dipped into the beaker, the string vibrates in its eleventh harmonic. Find the density of the material of the block.
The string of a guitar is 80 cm long and has a fundamental frequency of 112 Hz. If a guitarist wishes to produce a frequency of 160 Hz, where should the person press the string?
Use the formula `v = sqrt((gamma P)/rho)` to explain why the speed of sound in air is independent of pressure.
For the travelling harmonic wave
y (x, t) = 2.0 cos 2π (10t – 0.0080x + 0.35)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. Calculate the phase difference between oscillatory motion of two points separated by a distance of 4 m.
Speed of sound wave in air ______.
An engine is approaching a cliff at a constant speed. When it is at a distance of 0.9 km from cliff it sounds a whistle. The echo of the sound is heard by the driver after 5 seconds. Velocity of sound in air is equal to 330 ms-1. The speed of the engine is ______ km/h.
