Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Visible light passing through a circular hole forms a diffraction disc of radius 0.1 mm on a screen. If an X-ray is passed through the same setup, the radius of the diffraction disc will be
विकल्प
zero
< 0.1 mm
0.1 mm
> 0.1 m
उत्तर
< 0.1 mm
Radius of the diffraction disc is directly proportional to the wavelength of the light used for the given hole. We know that the wavelength of an X-ray is less than the wavelength of visible light. If an X-ray is passed through the same setup, the radius of the diffraction disc will be less than 0.1 m.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the region beyond the violet end of the spectrum called.
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with infrared rays.
Name two electromagnetic waves of frequency smaller than that of violet light. State one use of each.
The wavelength of X-rays is 0.01 Å. Calculate its frequency. State the assumption made, if any.
The Kα and Kβ X-rays of molybdenum have wavelengths 0.71 A and 0.63 A respectively. Find the wavelength of Lα X-ray of molybdenum.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
| Gamma rays | D | C | Visible light | B | A |
The above table shows different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
(a) Identify the parts of the spectrum marked as A, B, C and D.
(b) Which of the radiations A or B has the higher frequency?
(c) State two properties which are common to all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
(d) Name one source of each of the radiation of electromagnetic spectrum.
(e) Name one detector for each of the radiation.
(f) Name one use of each of the radiation.
Name the radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum which is used for the following:
Radar and Give the frequency range.
Name the radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum which is used for the following:
For taking photographs of the sky during the night and foggy conditions . Give the frequency range
Name any two electromagnetic waves which have a frequency higher than that of violet light. State one use of each.
How will you investigate the existence of the radiation beyond the red and violet extremes of the spectrum?
State two uses of infrared radiations.
Answer briefly.
Can we produce a pure electric or magnetic wave in space? Why?
A bat moving at 10 ms−1 towards a wall sends a sound signal of 8000 Hz towards it. On reflection, it hears a sound of frequency f The value of f in Hz is close to (speed of sound = 320 ms−1)
A car is moving towards a high cliff. The car driver sounds a horn of frequency f. The reflected sound heard by the driver has a frequency 2f. If v be the velocity of sound, then the velocity of the car, in the same velocity units, will be:
The fundamental frequency of an open organ pipe is 300 Hz. The first overtone of this pipe has same frequency as first overtone of a closed organ pipe. If speed of sound is 330 m/s, then the length of closed organ pipe is:
The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 100 W bulb at a 3 m distance is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 50 W bulb at the same distance is ______.
Give any two uses of infrared waves.
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
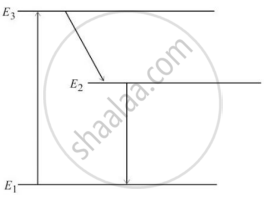
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
