Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following is a mechanical wave?
विकल्प
Radio waves
X-rays
Light waves
Sound waves.
उत्तर
Sound waves
There are mainly two types of waves: first is electromagnetic wave, which does not require any medium to travel, and the second is the mechanical wave, which requires a medium to travel. Sound requires medium to travel, hence it is a mechanical wave.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A cork floating in a calm pond executes simple harmonic motion of frequency
\[\nu\] when a wave generated by a boat passes by it. The frequency of the wave is
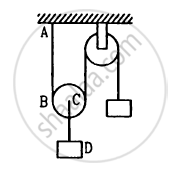
Both the strings, shown in figure, are made of same material and have same cross section. The pulleys are light. The wave speed of a transverse wave in the string AB is
\[\nu_1\] and in CD it is \[\nu_2\]. Then \[\nu_1 / \nu_2\]
Two periodic waves of amplitudes A1 and A2 pass thorough a region. If A1 > A2, the difference in the maximum and minimum resultant amplitude possible is
A wave is represented by the equation
\[y = \left( 0 \text{ cdot 001 mm }\right) \sin\left[ \left( 50 s^{- 1} \right)t + \left( 2 \cdot 0 m^{- 1} \right)x \right]\]
(a) The wave velocity = 100 m s−1.
(b) The wavelength = 2⋅0 m.
(c) The frequency = 25/π Hz.
(d) The amplitude = 0⋅001 mm.
A wave is described by the equation \[y = \left( 1 \cdot 0 mm \right) \sin \pi\left( \frac{x}{2 \cdot 0 cm} - \frac{t}{0 \cdot 01 s} \right) .\]
(a) Find the time period and the wavelength? (b) Write the equation for the velocity of the particles. Find the speed of the particle at x = 1⋅0 cm at time t = 0⋅01 s. (c) What are the speeds of the particles at x = 3⋅0 cm, 5⋅0 cm and 7⋅0 cm at t = 0⋅01 s?
(d) What are the speeds of the particles at x = 1⋅0 cm at t = 0⋅011, 0⋅012, and 0⋅013 s?
Find the change in the volume of 1.0 litre kerosene when it is subjected to an extra pressure of 2.0 × 105 N m−2 from the following data. Density of kerosene = 800 kg m−3and speed of sound in kerosene = 1330 ms−1.
In Quincke's experiment, the sound intensity has a minimum value l at a particular position. As the sliding tube is pulled out by a distance of 16.5 mm, the intensity increases to a maximum of 9 l. Take the speed of sound in air to be 330 m s−1. (a) Find the frequency of the sound source. (b) Find the ratio of the amplitudes of the two waves arriving at the detector assuming that it does not change much between the positions of minimum intensity and maximum intensity.
A closed organ pipe can vibrate at a minimum frequency of 500 Hz. Find the length of the tube. Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
A cylindrical metal tube has a length of 50 cm and is open at both ends. Find the frequencies between 1000 Hz and 2000 Hz at which the air column in the tube can resonate. Speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1.
An electronically driven loudspeaker is placed near the open end of a resonance column apparatus. The length of air column in the tube is 80 cm. The frequency of the loudspeaker can be varied between 20 Hz and 2 kHz. Find the frequencies at which the column will resonate. Speed of sound in air = 320 m s−1.
A U-tube having unequal arm-lengths has water in it. A tuning fork of frequency 440 Hz can set up the air in the shorter arm in its fundamental mode of vibration and the same tuning fork can set up the air in the longer arm in its first overtone vibration. Find the length of the air columns. Neglect any end effect and assume that the speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
A Kundt's tube apparatus has a steel rod of length 1.0 m clamped at the centre. It is vibrated in its fundamental mode at a frequency of 2600 Hz. The lycopodium powder dispersed in the tube collects into heaps separated by 6.5 cm. Calculate the speed of sound in steel and in air.
A tuning fork of unknown frequency makes 5 beats per second with another tuning fork which can cause a closed organ pipe of length 40 cm to vibrate in its fundamental mode. The beat frequency decreases when the first tuning fork is slightly loaded with wax. Find its original frequency. The speed of sound in air is 320 m s−1.
A person riding a car moving at 72 km h−1 sound a whistle emitting a wave of frequency 1250 Hz. What frequency will be heard by another person standing on the road (a) in front of the car (b) behind the car? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
A violin player riding on a slow train plays a 440 Hz note. Another violin player standing near the track plays the same note. When the two are closed by and the train approaches the person on the ground, he hears 4.0 beats per second. The speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1. (a) Calculate the speed of the train. (b) What beat frequency is heard by the player in the train?
A small source of sound vibrating at frequency 500 Hz is rotated in a circle of radius 100/π cm at a constant angular speed of 5.0 revolutions per second. A listener situation situates himself in the plane of the circle. Find the minimum and the maximum frequency of the sound observed. Speed of sound in air = 332 m s−1.
Two submarines are approaching each other in a calm sea. The first submarine travels at a speed of 36 km h−1 and the other at 54 km h−1 relative to the water. The first submarine sends a sound signal (sound waves in water are also called sonar) at a frequency of 2000 Hz. (a) At what frequency is this signal received from the second submarine. At what frequency is this signal received by the first submarine. Take the speed of of the sound wave in water to be 1500 m s−1.
A source emitting sound at frequency 4000 Hz, is moving along the Y-axis with a speed of 22 m s−1. A listener is situated on the ground at the position (660 m, 0). Find the frequency of the sound received by the listener at the instant the source crosses the origin. Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
The speed of sound in hydrogen is 1270 m/s. The speed of sound in the mixture of oxygen and hydrogen in which they are mixed in 1:4 ratio is
Change in temperature of the medium changes ______.
