Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Polynomials
▶ 3: Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable
4: Quadatric Euation
5: Arithematic Progressions
6: Triangles
7: Coordinate Geometry
8: Introduction To Trigonometry and Its Applications
9: Circles
10: Construction
11: Area Related To Circles
12: Surface Areas and Volumes
13: Statistics and Probability
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Mathematics [English] Class 10.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 3 Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable Exercise 3.1 [Pages 18 - 19]
Choose the correct alternative:
Graphically, the pair of equations 6x – 3y + 10 = 0, 2x – y + 9 = 0 represents two lines which are ______.
Intersecting at exactly one point
Intersecting at exactly two points
Coincident
Parallel
The pair of equations x + 2y + 5 = 0 and –3x – 6y + 1 = 0 have ______.
A unique solution
Exactly two solutions
Infinitely many solutions
No solution
If a pair of linear equations is consistent, then the lines will be ______.
Parallel
Always coincident
Intersecting or coincident
Always intersecting
The pair of equations y = 0 and y = –7 has ______.
One solution
Two solutions
Infinitely many solutions
No solution
The pair of equations x = a and y = b graphically represents lines which are ______.
Parallel
Intersecting at (b, a)
Coincident
Intersecting at (a, b)
For what value of k, do the equations 3x – y + 8 = 0 and 6x – ky = –16 represent coincident lines?
`1/2`
`-1/2`
2
–2
If the lines given by 3x + 2ky = 2 and 2x + 5y + 1 = 0 are parallel, then the value of k is ______.
`(-5)/4`
`2/5`
`15/4`
`3/2`
The value of c for which the pair of equations cx – y = 2 and 6x – 2y = 3 will have infinitely many solutions is ______.
3
– 3
–12
No value
One equation of a pair of dependent linear equations is –5x + 7y = 2. The second equation can be ______.
10x + 14y + 4 = 0
–10x – 14y + 4 = 0
–10x + 14y + 4 = 0
10x – 14y = –4
A pair of linear equations which has a unique solution x = 2, y = –3 is ______.
x + y = –1, 2x – 3y = –5
2x + 5y = –11, 4x + 10y = –22
2x – y = 1, 3x + 2y = 0
x – 4y –14 = 0, 5x – y – 13 = 0
If x = a, y = b is the solution of the equations x – y = 2 and x + y = 4, then the values of a and b are, respectively ______.
3 and 5
5 and 3
3 and 1
–1 and –3
Aruna has only Rs 1 and Rs 2 coins with her. If the total number of coins that she has is 50 and the amount of money with her is Rs 75, then the number of Rs 1 and Rs 2 coins are, respectively ______.
35 and 15
35 and 20
15 and 35
25 and 25
The father’s age is six times his son’s age. Four years hence, the age of the father will be four times his son’s age. The present ages, in years, of the son and the father are, respectively ______.
4 and 24
5 and 30
6 and 36
3 and 24
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 3 Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable Exercise 3.2 [Pages 21 - 22]
Do the following pair of linear equations have no solution? Justify your answer.
2x + 4y = 3, 12y + 6x = 6
Do the following pair of linear equations have no solution? Justify your answer.
x = 2y, y = 2x
Do the following pair of linear equations have no solution? Justify your answer.
`3x + y - 3 = 0, 2x + 2/3y = 2`
Do the following equations represent a pair of coincident lines? Justify your answer.
`3x + 1/7 y = 3, 7x + 3y = 7`
Do the following equations represent a pair of coincident lines? Justify your answer.
–2x – 3y = 1, 6y + 4x = – 2
Do the following equations represent a pair of coincident lines? Justify your answer.
`x/2 + y + 2/5` = 0, `4x + 8y + 5/16` = 0
Are the following pair of linear equations consistent? Justify your answer.
–3x – 4y = 12, 4y + 3x = 12
Are the following pair of linear equations consistent? Justify your answer.
`3/5x - y = 1/2, 1/5x - 3y = 1/6`
Are the following pair of linear equations consistent? Justify your answer.
2ax + by = a, 4ax + 2by – 2a = 0; a, b ≠ 0
Are the following pair of linear equations consistent? Justify your answer.
x + 3y = 11, 2(2x + 6y) = 22
For the pair of equations λx + 3y = –7, 2x + 6y = 14 to have infinitely many solutions, the value of λ should be 1. Is the statement true? Give reasons.
For all real values of c, the pair of equations x – 2y = 8, 5x – 10y = c have a unique solution. Justify whether it is true or false.
True
False
The line represented by x = 7 is parallel to the x–axis. Justify whether the statement is true or not.
True
Not true
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 3 Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable Exercise 3.3 [Pages 25 - 28]
For which value(s) of λ, do the pair of linear equations λx + y = λ2 and x + λy = 1 have no solution?
For which value(s) of λ, do the pair of linear equations λx + y = λ2 and x + λy = 1 have infinitely many solutions?
For which value(s) of λ, do the pair of linear equations λx + y = λ2 and x + λy = 1 have a unique solution?
For which value(s) of k will the pair of equations kx + 3y = k – 3, 12x + ky = k have no solution?
For which values of a and b, will the following pair of linear equations have infinitely many solutions?
x + 2y = 1, (a – b)x + (a + b)y = a + b – 2
Find the value(s) of p in (i) to (iv) and p and q in (v) for the following pair of equations:
3x – y – 5 = 0 and 6x – 2y – p = 0,
if the lines represented by these equations are parallel.
Find the value(s) of p in (i) to (iv) and p and q in (v) for the following pair of equations:
– x + py = 1 and px – y = 1,
if the pair of equations has no solution.
Find the value(s) of p in (i) to (iv) and p and q in (v) for the following pair of equations:
– 3x + 5y = 7 and 2px – 3y = 1,
if the lines represented by these equations are intersecting at a unique point.
Find the value(s) of p in (i) to (iv) and p and q in (v) for the following pair of equations:
2x + 3y – 5 = 0 and px – 6y – 8 = 0,
if the pair of equations has a unique solution.
Find the value(s) of p in (i) to (iv) and p and q in (v) for the following pair of equations:
2x + 3y = 7 and 2px + py = 28 – qy,
if the pair of equations have infinitely many solutions.
Two straight paths are represented by the equations x – 3y = 2 and –2x + 6y = 5. Check whether the paths cross each other or not.
Write a pair of linear equations which has the unique solution x = – 1, y = 3. How many such pairs can you write?
If 2x + y = 23 and 4x – y = 19, find the values of 5y – 2x and `y/x` – 2.
Find the values of x and y in the following rectangle [see figure].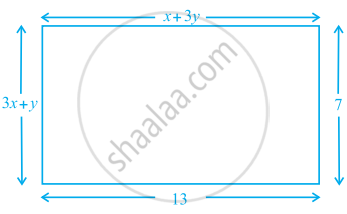
Solve the following pair of equations:
x + y = 3.3, `0.6/(3x - 2y) = -1, 3x - 2y ≠ 0`
Solve the following pair of equations:
`x/3 + y/4 = 4, (5x)/6 - y/4 = 4`
Solve the following pair of equations:
`4x + 6/y = 15, 6x - 8/y = 14, y ≠ 0`
Solve the following pair of equations:
`1/(2x) - 1/y = -1, 1/x + 1/(2y) = 8, x, y ≠ 0`
Solve the following pair of equations:
43x + 67y = – 24, 67x + 43y = 24
Solve the following pair of equations:
`x/a + y/b = a + b, x/a^2 + y/b^2 = 2, a, b ≠ 0`
Solve the following pair of equations:
`(2xy)/(x + y) = 3/2, (xy)/(2x - y) = (-3)/10, x + y ≠ 0, 2x - y ≠ 0`
Find the solution of the pair of equations `x/10 + y/5 - 1` = 0 and `x/8 + y/6` = 15. Hence, find λ, if y = λx + 5.
By the graphical method, find whether the following pair of equations are consistent or not. If consistent, solve them.
3x + y + 4 = 0, 6x – 2y + 4 = 0
By the graphical method, find whether the following pair of equations are consistent or not. If consistent, solve them.
x – 2y = 6, 3x – 6y = 0
By the graphical method, find whether the following pair of equations are consistent or not. If consistent, solve them.
x + y = 3, 3x + 3y = 9
Draw the graph of the pair of equations 2x + y = 4 and 2x – y = 4. Write the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and the y-axis. Also find the area of this triangle.
Write an equation of a line passing through the point representing solution of the pair of linear equations x + y = 2 and 2x – y = 1. How many such lines can we find?
If (x + 1) is a factor of 2x3 + ax2 + 2bx + 1, then find the values of a and b given that 2a – 3b = 4.
The angles of a triangle are x, y and 40°. The difference between the two angles x and y is 30°. Find x and y.
Two years ago, Salim was thrice as old as his daughter and six years later, he will be four years older than twice her age. How old are they now?
The age of the father is twice the sum of the ages of his two children. After 20 years, his age will be equal to the sum of the ages of his children. Find the age of the father.
Two numbers are in the ratio 5 : 6. If 8 is subtracted from the numbers, the ratio becomes 4 : 5. Find the numbers.
There are some students in the two examination halls A and B. To make the number of students equal in each hall, 10 students are sent from A to B. But if 20 students are sent from B to A, the number of students in A becomes double the number of students in B. Find the number of students in the two halls.
A shopkeeper gives books on rent for reading. She takes a fixed charge for the first two days, and an additional charge for each day thereafter. Latika paid Rs 22 for a book kept for six days, while Anand paid Rs 16 for the book kept for four days. Find the fixed charges and the charge for each extra day.
In a competitive examination, one mark is awarded for each correct answer while `1/2` mark is deducted for every wrong answer. Jayanti answered 120 questions and got 90 marks. How many questions did she answer correctly?
The angles of a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD are ∠A = (6x + 10)°, ∠B = (5x)°, ∠C = (x + y)°, ∠D = (3y – 10)°. Find x and y, and hence the values of the four angles.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 3 Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable Exercise 3.4 [Pages 33 - 34]
Graphically, solve the following pair of equations:
2x + y = 6, 2x – y + 2 = 0
Find the ratio of the areas of the two triangles formed by the lines representing these equations with the x-axis and the lines with the y-axis.
Determine, graphically, the vertices of the triangle formed by the lines y = x, 3y = x, x + y = 8
Draw the graphs of the equations x = 3, x = 5 and 2x – y – 4 = 0. Also find the area of the quadrilateral formed by the lines and the x–axis.
The cost of 4 pens and 4 pencil boxes is Rs 100. Three times the cost of a pen is Rs 15 more than the cost of a pencil box. Form the pair of linear equations for the above situation. Find the cost of a pen and a pencil box.
Determine, algebraically, the vertices of the triangle formed by the lines
3x – y = 2
2x – 3y = 2
x + 2y = 8
Ankita travels 14 km to her home partly by rickshaw and partly by bus. She takes half an hour if she travels 2 km by rickshaw, and the remaining distance by bus. On the other hand, if she travels 4 km by rickshaw and the remaining distance by bus, she takes 9 minutes longer. Find the speed of the rickshaw and of the bus.
A person, rowing at the rate of 5 km/h in still water, takes thrice as much time in going 40 km upstream as in going 40 km downstream. Find the speed of the stream.
A motor boat can travel 30 km upstream and 28 km downstream in 7 hours. It can travel 21 km upstream and return in 5 hours. Find the speed of the boat in still water and the speed of the stream.
A two-digit number is obtained by either multiplying the sum of the digits by 8 and then subtracting 5 or by multiplying the difference of the digits by 16 and then adding 3. Find the number.
A railway half ticket costs half the full fare, but the reservation charges are the same on a half ticket as on a full ticket. One reserved first class ticket from the station A to B costs Rs 2530. Also, one reserved first class ticket and one reserved first class half ticket from A to B costs Rs 3810. Find the full first class fare from station A to B, and also the reservation charges for a ticket.
A shopkeeper sells a saree at 8% profit and a sweater at 10% discount, thereby, getting a sum Rs 1008. If she had sold the saree at 10% profit and the sweater at 8% discount, she would have got Rs 1028. Find the cost price of the saree and the list price (price before discount) of the sweater.
Susan invested certain amount of money in two schemes A and B, which offer interest at the rate of 8% per annum and 9% per annum, respectively. She received Rs 1860 as annual interest. However, had she interchanged the amount of investments in the two schemes, she would have received Rs 20 more as annual interest. How much money did she invest in each scheme?
Vijay had some bananas, and he divided them into two lots A and B. He sold the first lot at the rate of Rs 2 for 3 bananas and the second lot at the rate of Re 1 per banana, and got a total of Rs 400. If he had sold the first lot at the rate of Re 1 per banana, and the second lot at the rate of Rs 4 for 5 bananas, his total collection would have been Rs 460. Find the total number of bananas he had.
Solutions for 3: Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 CBSE 3 (Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 3 Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable are Relation Between Co-efficient, Inconsistency of Pair of Linear Equations, Algebraic Conditions for Number of Solutions, Simple Situational Problems, Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables, Substitution Method, Elimination Method, Consistency of Pair of Linear Equations, Graphical Method, Introduction to linear equations in two variables, Cross - Multiplication Method, Equations Reducible to a Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables.
Using NCERT Exemplar Mathematics [English] Class 10 solutions Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 10 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Pair of Liner Equation in Two Variable Mathematics [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
