Topics
Historiography : Development in the West
History : Applied History
Working of the Constitution
Historiography : Indian Tradition
The Electoral Process
Political Science : Working of the Indian Constitution
Applied History
Political Parties
History of Indian Arts
- What is ‘Art’?
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Painting
- Prehistoric Paintings
- Mural Paintings and Cave Painting
- Folk Styles of Paintings
- Classical Styles of Painting
- Miniature Paintings in Manuscripts
- Modern Indian Paintings
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Sculpture Art
- Indus Civilization Sculpture
- Folk Styles of Sculptural Art
- Classical Styles of Sculptural Art
- Indian Iconography
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Architecture and Sculpture
- Rock-cut Architecture
- Temple Architecture
- Indo-Islamic Architecture
- Indo-Gothic architecture
- Indian Traditions of Performing Arts
- Indian Theatre
- Indian Music
- Indian Dance
- Present Scenario of the Performing Arts
- Art, Applied Art, and Professional Opportunities
Social and Political Movements
- Movement
- Important Movements in India
- Tribal Movement
- Farmers Movement
- Worker's Movements
- Women’s Movement
- Environment Movements
- Consumer Movement
Mass Media and History
Challenges Faced by Indian Democracy
Entertainment and History
Sports and History
Tourism and History
Heritage Management
History - Imperialism
History - 20th Century Age of conflict
History - Emancipation of Asia and Africa
History - World after World War 2
Political Science
Geographical discoveries and colonization
- Concept for Geographical Discoveries and Colonization
Africa
- Imperialism - Africa
Asia: India, China, Japan
- Concept for Asia: India, China, Japan
Dictatorships in Europe, Second World War and world
- Concept on Dictatorships in Europe
- Concept for Second World War and World
First world war
- Concept on First World War
The League of Nations
- Concept for the League of Nations
Russian Revolution
- Concept for Russian Revolution
United Nations Organization
- Concept for United Nations Organization
Africa
- Emancipation of Africa
Asia
- Emancipation of Asia
Globalization
- Globalization After World War II
Scientific and Technological Progress
- Scientific and Technological Progress After World War II
Cold war
- Formation of the Cold War
Social Diversity and Democracy
- Social Diversity
- Coccept for Caste/Race and Democracy
- Concept for Language and Democracy
- Cocnept for Religion and Democracy
- Concept for Gender and Democracy
- Concept for Democracy and Diversity
Challenges to Democracy Remedial Measures to the Challenges
- Concept for Challenges to Democracy Remedial Measures to the Challenges
Internal work
Democracy
- Democracy - Meaning, Types and Characteristics
Political Parties and Types
- Political Parties
- Importance of Political Parties
- Major National and Regional Parties in India/ Types of Political Parties
- Maratha style painting
- Warli painting
- Chitrakathi tradition
Notes
Folk Styles of Paintings
- Folk styles of painting generally depict the lifestyle, culture, tradition, etc., of a particular place or region.
- The folk group is a function of shared community-based identity, not of individualism.
- They are pictorial expressions of village painters which are marked by the subjects chosen from the epics like Ramayana and Mahabharata, Bhagvat Purana as well as daily village life, birds and animals, and natural objects like sun, moon, plants, and trees.
- The tradition of folk art has a style that is very similar to that of rock art.
- Regional folk painting styles were influenced by practices like Rangawali, which involved decorating houses and courtyards with diverse figures and symbols or telling stories with panels of paintings.
Types of Folk styles of paintings:
1. Maratha Style Painting:
| Maratha Style Folk Painting | |
|
Durbar hall |
Coronation of Shivaji Maharaj |
- Maratha painting is an example of a type of art. The Maratha painting style emerged in the latter half of the 17th century C.E.
- This style comprises colored paintings that appear as murals as well as miniatures in manuscripts.
- Maratha-style murals can be found in old wadas in Maharashtra, such as Wai, Menavali, and Satara.
- The Rajput and European painting styles impacted the Maratha style.
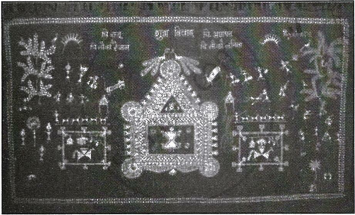
2. Warli Style of Painting:
|
Warli Painting, Maharashtra |
- Warli painting is a form of tribal art mostly created by the tribal people from the North Sahyadri Range in Maharashtra with a large concentration in the district of Thane.
- The basic characters used in Warli paintings are a circle, a triangle, and a square placed at different angles. Triangles linked at the tip are used to depict humans, animal bodies, and other items.
- The Warli paintings portray the tribe's day-to-day activities and hence are largely based on harvest festivals, folk stories, celebrations in temples, marriage, and so on.
- The paintings were created on the red mud walls of huts. The ochre-colored walls are painted with a rice-and-water mixture. They drew the paintings with crooked bamboo sticks as paintbrushes.
- After 1970, Warli paintings were well-known throughout the world. Jivya Somya Mashe, the artist who popularised the artwork over the world, has been honored with Padma Shri in 2011 and many national and international awards. He died on May 15, 2018.
3. Chitrakathi Tradition:
|
Leather shadow puppets |
Picture stories |
- The Chitrakathi also known as Pinguli tradition is the name of an occupational caste whose traditional livelihood was to narrate stories aided with pictures of sojourning various places.
- "Chitra" means picture and "katha" means story and the exponent called Chitrakathi is the person who narrates the story with the aid of some visual support.
- They sing the tale while showing it visually using pictures. "Broadly speaking, Chitrakatha is identified in three forms, Leather shadow puppets, Stringed wooden puppets, and Picture stories.
- They made a series of single sheets of paintings. All paintings belonging to one story were kept in a bundle called "pothi".
- Chitrakathi artists are a community of storytellers found all over Maharashtra and some parts of Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.
- This mostly depicts the gods and royals. The Theme of Chitrakathi paintings includes stories on local versions of Ramayana and Mahabharata and mythical themes.
- The Chalukya ruler Someshvara's book 'Manasollas’, also known as Abhilashitartha Chintamani, which was published in the 12th century C.E., mentions the tradition of Chitrakathi.

Stringed wooden puppets
- The Chitrakathi images are painted with natural-color paints on a piece of paper. The narration of one story is completed in 30-50 images. These photographs have been passed down from one generation to the next and are carefully preserved.
- The tradition, which is in danger of dying out, is being preserved by artists and the government.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.