Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A collision experiment is done on a horizontal table kept in an elevator. Do you expect a change in the result if the elevator is accelerated up or down because of the noninertial character of the frame?
उत्तर
No. As the collision experiment is being done on a horizontal table in the elevator that is accelerating up or down in vertical direction, no extra force is experienced in the horizontal direction. Hence, the objects in the horizontal direction remain unaffected.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the HCl molecule, the separation between the nuclei of the two atoms is about 1.27 Å (1 Å = 10–10 m). Find the approximate location of the CM of the molecule, given that a chlorine atom is about 35.5 times as massive as a hydrogen atom and nearly all the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus.
You are waiting for a train on a railway platform. Your three-year-old niece is standing on your iron trunk containing the luggage. Why does the trunk not recoil as she jumps off on the platform?
You are holding a cage containing a bird. Do you have to make less effort if the bird flies from its position in the cage and manages to stay in the middle without touching the walls of the cage? Does it makes a difference whether the cage is completely closed or it has rods to let air pass?
Consider the following two statements:
(A) Linear momentum of the system remains constant.
(B) Centre of mass of the system remains at rest.
In an elastic collision
The centre of mass of a system of particles is at the origin. It follows that
Two balls are thrown simultaneously in air. The acceleration of the centre of mass of the two balls while in air
A square plate of edge d and a circular disc of diameter d are placed touching each other at the midpoint of an edge of the plate as shown in figure. Locate the centre of mass of the combination, assuming same mass per unit area for the two plates.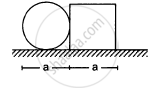
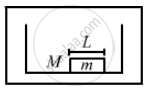
Consider a gravity-free hall in which a tray of mass M, carrying a cubical block of ice of mass m and edge L, is at rest in the middle. If the ice melts, by what distance does the centre of mass of "the tray plus the ice" system descend?
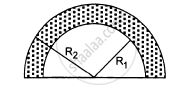
Find the centre of mass of a uniform plate having semicircular inner and outer boundaries of radii R1 and R2.
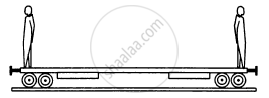
Two persons each of mass m are standing at the two extremes of a railroad car of mass M resting on a smooth track(In the following figure). The person on left jumps to the left with a horizontal speed u with respect to the state of the car before the jump. Thereafter, the other person jumps to the right, again with the same horizontal speed u with respect to the state of the car before his jump. Find the velocity of the car after both the persons have jumped off.
The axis of rotation of a purely rotating body
(a) must pass through the centre of mass
(b) may pass through the centre of mass
(c) must pass through a particle of the body
(d) may pass through a particle of the body.
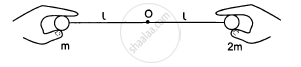
Two balls having masses m and 2m are fastened to two light strings of same length l (See figure). The other ends of the strings are fixed at O. The strings are kept in the same horizontal line and the system is released from rest. The collision between the balls is elastic. (a) Find the velocity of the balls just after their collision. (b) How high will the ball rise after the collision?
Find out the centre of mass for the given geometrical structures.
a) Equilateral triangle
b) Cylinder
c) Square
A shell of mass 'M' initially at rest suddenly explodes in three fragments. Two of these fragments are of mass 'M/4' each, which move with velocities 3 ms-1 and 4 ms-1 respectively in mutually perpendicular directions. The magnitude of velocity of the third fragment is ______.
The density of a non-uniform rod of length 1 m is given by ρ(x) = a(1 + bx2) where a and b are constants and 0 ≤ x ≤ 1. The centre of mass of the rod will be at ______.
A uniform square plate S (side c) and a uniform rectangular plate R (sides b, a) have identical areas and masses (Figure).
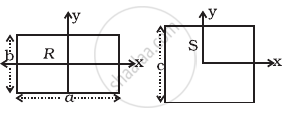
Show that
- IxR/IxS < 1
- IyR/IyS > 1
- IzR/IzS > 1
The mass per unit length of a non-uniform rod of length L varies as m = λx where λ is constant. The centre of mass of the rod will be at ______.
