Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The axis of rotation of a purely rotating body
(a) must pass through the centre of mass
(b) may pass through the centre of mass
(c) must pass through a particle of the body
(d) may pass through a particle of the body.
उत्तर
(b) may pass through the centre of mass
(d) may pass through a particle of the body
It is not necessary that the axis of rotation of a purely rotating body should pass through the centre of mass or through a particle of the body. It can also lie outside the body.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A child sits stationary at one end of a long trolley moving uniformly with a speed V on a smooth horizontal floor. If the child gets up and runs about on the trolley in any manner, what is the speed of the CM of the (trolley + child) system?
Consider the following two statements:
(A) Linear momentum of the system remains constant.
(B) Centre of mass of the system remains at rest.
In an elastic collision
Three particles of masses 1.0 kg, 2.0 kg and 3.0 kg are placed at the corners A, B and C respectively of an equilateral triangle ABC of edge 1 m. Locate the centre of mass of the system.
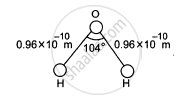
The structure of a water molecule is shown in figure. Find the distance of the centre of mass of the molecule from the centre of the oxygen atom.
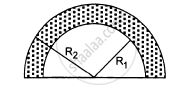
Find the centre of mass of a uniform plate having semicircular inner and outer boundaries of radii R1 and R2.
In an elastic collision
A railroad car of mass M is at rest on frictionless rails when a man of mass m starts moving on the car towards the engine. If the car recoils with a speed v backward on the rails, with what velocity is the man approaching the engine?
A particle of mass 100 g moving at an initial speed u collides with another particle of same mass kept initially at rest. If the total kinetic energy becomes 0.2 J after the collision, what could be the minimum and the maximum value of u.
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose each of the blocks is pulled by a constant force F instead of any impulse. Find the maximum elongation that the spring will suffer and the distance moved by the two blocks in the process.
A round object of mass M and radius R rolls down without slipping along an inclined plane. The frictional force, ______
The speed of the centre of a wheel rolling on a horizontal surface is vo. A point on the rim is level with the centre will be moving at a speed of, ______
A body of mass 2 kg is acted upon by two forces each of magnitude 1 N and inclined at 60° with each other. The acceleration of the body in m/s is ____________. [cos 60° = 0.5]
The centre of mass of a right circular cone of height h, radius R and constant density `sigma` is at ____________.
A mass of 1kg is suspended by a string. It is first lifted up with an acceleration of 4.9 m/s2 and then lowered down with same acceleration. The ratio of tensions in the string in the two cases, respectively is g = 9.8 m/s2 ______.
A shell of mass 'M' initially at rest suddenly explodes in three fragments. Two of these fragments are of mass 'M/4' each, which move with velocities 3 ms-1 and 4 ms-1 respectively in mutually perpendicular directions. The magnitude of velocity of the third fragment is ______.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(n – 1) equal point masses each of mass m are placed at the vertices of a regular n-polygon. The vacant vertex has a position vector a with respect to the centre of the polygon. Find the position vector of centre of mass.
Find the centre of mass of a uniform (a) half-disc, (b) quarter-disc.
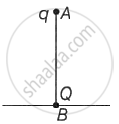
A point charge Q is situated at point B on the ground. A point charge q of mass m is vertically dropped along line AB from a multi-storey building of height h. Find the position of the point charge q when it is in equilibrium.