Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Three particles of masses 1.0 kg, 2.0 kg and 3.0 kg are placed at the corners A, B and C respectively of an equilateral triangle ABC of edge 1 m. Locate the centre of mass of the system.
उत्तर
Taking BC as the X-axis and point B as the origin, the positions of masses m1 = 1 kg, m2= 2 kg and m3 = 3 kg are
\[\left( 0, 0 \right), \left( 1, 0 \right) \text{ and }\left( \frac{1}{2}, \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)\] respectively.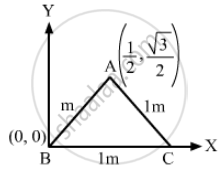
The position of centre of mass is given by:
\[X_{cm} , Y_{cm} = \frac{m_1 x_1 + m_2 x_2 + m_3 x_3}{m_1 + m_2 + m_3}, \frac{m_1 y_1 + m_2 y_2 + m_3 y_3}{m_1 + m_2 + m_3}\]
\[= \frac{1 \times 0 + 2 \times 1 + 3 \times \frac{1}{2}}{1 + 2 + 3}, \frac{1 \times 0 + 2 \times 0 + 3 \times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}}{1 + 2 + 3}\]
\[ = \frac{7}{12} m, \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} m\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A collision experiment is done on a horizontal table kept in an elevator. Do you expect a change in the result if the elevator is accelerated up or down because of the noninertial character of the frame?
A high-jumper successfully clears the bar. Is it possible that his centre of mass crossed the bar from below it? Try it with appropriate figures.
A circular plate of diameter d is kept in contact with a square plate of edge d as show in figure. The density of the material and the thickness are same everywhere. The centre of mass of the composite system will be 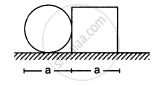
If the external force acting on a system have zero resultant, the centre of mass
(a) must not move
(b) must not accelerate
(c) may move
(d) may accelerate.
A nonzero external force acts on a system of particles. The velocity and the acceleration of the centre of mass are found to be v0 and a0 at instant t. It is possible that
(a) v0 = 0, a0 = 0
(b) v0 = 0, a0 ≠ 0
(c) v0 ≠ 0, a0 = 0
(d) v0 ≠ 0, a0 ≠ 0
Seven homogeneous bricks, each of length L, are arranged as shown in figure. Each brick is displaced with respect to the one in contact by L/10. Find the x-coordinate fo the centre of mass relative to the origin shown.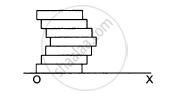
A square plate of edge d and a circular disc of diameter d are placed touching each other at the midpoint of an edge of the plate as shown in figure. Locate the centre of mass of the combination, assuming same mass per unit area for the two plates.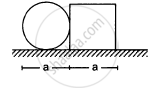
Mr. Verma (50 kg) and Mr. Mathur (60 kg) are sitting at the two extremes of a 4 m long boat (40 kg) standing still in water. To discuss a mechanics problem, they come to the middle of the boat. Neglecting friction with water, how far does the boat move on the water during the process?
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose each of the blocks is pulled by a constant force F instead of any impulse. Find the maximum elongation that the spring will suffer and the distance moved by the two blocks in the process.
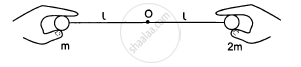
Two balls having masses m and 2m are fastened to two light strings of same length l (See figure). The other ends of the strings are fixed at O. The strings are kept in the same horizontal line and the system is released from rest. The collision between the balls is elastic. (a) Find the velocity of the balls just after their collision. (b) How high will the ball rise after the collision?
A mass of 1kg is suspended by a string. It is first lifted up with an acceleration of 4.9 m/s2 and then lowered down with same acceleration. The ratio of tensions in the string in the two cases, respectively is g = 9.8 m/s2 ______.
The ratio of weights of a man inside a lift when it is stationary and when it is going down with a uniform acceleration 'a' is 3 : 2. The value of 'a' will be ______.
(a< g, g = acceleration due to gravity)
Which of the following points is the likely position of the centre of mass of the system shown in figure?
A uniform square plate has a small piece Q of an irregular shape removed and glued to the centre of the plate leaving a hole behind figure. The CM of the plate is now in the following quadrant of x-y plane ______.
Figure shows a lamina in x-y plane. Two axes z and z ′ pass perpendicular to its plane. A force F acts in the plane of lamina at point P as shown. Which of the following are true? (The point P is closer to z′-axis than the z-axis.)

- Torque τ caused by F about z axis is along `-hatk`.
- Torque τ′ caused by F about z′ axis is along `-hatk`.
- Torque τ caused by F about z axis is greater in magnitude than that about z axis.
- Total torque is given be τ = τ + τ′.
A uniform square plate S (side c) and a uniform rectangular plate R (sides b, a) have identical areas and masses (Figure).
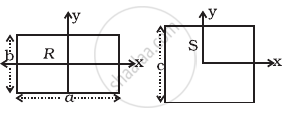
Show that
- IxR/IxS < 1
- IyR/IyS > 1
- IzR/IzS > 1
The mass per unit length of a non-uniform rod of length L varies as m = λx where λ is constant. The centre of mass of the rod will be at ______.
The spheres of masses 2 kg and 4 kg are situated at the opposite ends of wooden bars of length 9 m. Where does the centre of mass of the system will ______.
