Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A farmer has a 100 acre farm. He can sell the tomatoes, lettuce, or radishes he can raise. The price he can obtain is Rs 1 per kilogram for tomatoes, Rs 0.75 a head for lettuce and Rs 2 per kilogram for radishes. The average yield per acre is 2000 kgs for radishes, 3000 heads of lettuce and 1000 kilograms of radishes. Fertilizer is available at Rs 0.50 per kg and the amount required per acre is 100 kgs each for tomatoes and lettuce and 50 kilograms for radishes. Labour required for sowing, cultivating and harvesting per acre is 5 man-days for tomatoes and radishes and 6 man-days for lettuce. A total of 400 man-days of labour are available at Rs 20 per man-day. Formulate this problem as a LPP to maximize the farmer's total profit.
उत्तर
Let the farmer sow tomatoes in x acres, lettuce in y acres & radishes in z acres of the farm.
Average yield per acre is 2000 kgs for tomatoes, 3000 kgs of lettuce and 1000 kg of radishes.
Thus, the farmer raised 2000x kg of tomatoes, 3000y kg of lettuce and 1000z kg of radishes.
Given, price he can obtain is Re 1 per kilogram for tomatoes, Re 0.75 a head for lettuce and Rs 2 per kilogram for radishes.
∴ Selling price = Rs \[\left[ 2000x\left( 1 \right) + 3000y\left( 0 . 75 \right) + 1000z\left( 2 \right) \right]\] = Rs (2000x + 2250y + 2000z)
Labour required for sowing, cultvating and harvesting per acre is 5 man-days for tomatoes and radishes and 6 man-days for lettuce.Therefore, labour required for sowing, cultivating and harvesting per acre is 5x for tomatoes, 6y for lettuce and 5z for radishes.
Number of man-days required in sowing, cultivating and harvesting= \[5x + 6y + 5z\] Price of one man-day = Rs 20
Therefore, fertilizer required is 100x kgs for the tomatoes sown in x acres, 100y kgs for the lettuce sown in y acres and 50z kgs for radishes sown in z acres of land.
Hence, total fertilizer used= (100x + 100y +50z) kgs
Thus, fertilizer's cost =
= Rs
= Rs\[\left( 1850x + 2080y + 1875z \right)\]
Let Z denotes the total profit
Total area of the farm = 100 acres
Also, it is given that the total man-days available are 400.
Thus, \[5x + 6y + 5z \leq 400\]
Area of the land cannot be negative.
Therefore, \[x, y \geq 0\]
Hence, the required LPP is as follows:
Maximize \[Z = 1850x + 2080y + 1875z\]
\[x + y + z \leq 100\]
\[ 5x + 6y + 5z \leq 400\]
\[x, y, z \geq 0\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A company produces two types of goods A and B, that require gold and silver. Each unit of type A requires 3 g of silver and 1 g of golds while that of type B requires 1 g of silver and 2 g of gold. The company can procure a maximum of 9 g of silver and 8 g of gold. If each unit of type A brings a profit of Rs 40 and that of type B Rs 50, formulate LPP to maximize profit.
A firm manufactures two products, each of which must be processed through two departments, 1 and 2. The hourly requirements per unit for each product in each department, the weekly capacities in each department, selling price per unit, labour cost per unit, and raw material cost per unit are summarized as follows:
| Product A | Product B | Weekly capacity | |
| Department 1 | 3 | 2 | 130 |
| Department 2 | 4 | 6 | 260 |
| Selling price per unit | ₹ 25 | ₹ 30 | |
| Labour cost per unit | ₹ 16 | ₹ 20 | |
| Raw material cost per unit | ₹ 4 | ₹ 4 |
The problem is to determine the number of units to produce each product so as to maximize total contribution to profit. Formulate this as a LPP.
Solve the following L.P.P. by graphical method :
Maximize : Z = 7x + 11y subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 26, 5x + 3y ≤ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following L.P.P. by graphical method :
Maximize: Z = 3x + 5y subject to x + 4y ≤ 24, 3x + y ≤ 21, x + y ≤ 9, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 also find maximum value of Z.
Solve the following L.P.P. by graphical method :
Minimize : Z = 7x + y subject to 5x + y ≥ 5, x + y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Choose the correct alternative:
The value of objective function is maximize under linear constraints.
Fill in the blank :
Graphical solution set of the in equations x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is in _______ quadrant
Fill in the blank :
The region represented by the in equations x ≤ 0, y ≤ 0 lines in _______ quadrants.
The constraint that a factory has to employ more women (y) than men (x) is given by _______
The region represented by the inequalities x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 lies in first quadrant.
Graphical solution set of x ≤ 0, y ≥ 0 in xy system lies in second quadrant.
Solve the following problem :
Maximize Z = 4x1 + 3x2 Subject to 3x1 + x2 ≤ 15, 3x1 + 4x2 ≤ 24, x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0
Choose the correct alternative:
If LPP has optimal solution at two point, then
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The maximum value of Z = 5x + 3y subjected to constraints 3x + y ≤ 12, 2x + 3y ≤ 18, 0 ≤ x, y is 20
State whether the following statement is True or False:
A convex set includes the points but not the segment joining the points
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The point (6, 4) does not belong to the feasible region bounded by 8x + 5y ≤ 60, 4x + 5y ≤ 40, 0 ≤ x, y
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The graphical solution set of the inequations 0 ≤ y, x ≥ 0 lies in second quadrant
A dealer deals in two products X and Y. He has ₹ 1,00,000/- to invest and space to store 80 pieces. Product X costs ₹ 2500/- and product Y costs ₹ 1000/- per unit. He can sell the items X and Y at respective profits of ₹ 300 and ₹ 90. Construct the LPP and find the number of units of each product to be purchased to maximize its profit
A company manufactures two types of ladies dresses C and D. The raw material and labour available per day is given in the table.
| Resources | Dress C(x) | Dress D(y) | Max. availability |
| Raw material | 5 | 4 | 60 |
| Labour | 5 | 3 | 50 |
P is the profit, if P = 50x + 100y, solve this LPP to find x and y to get the maximum profit
Smita is a diet conscious house wife, wishes to ensure certain minimum intake of vitamins A, B and C for the family. The minimum daily needs of vitamins A, B, and C for the family are 30, 20, and 16 units respectively. For the supply of the minimum vitamin requirements Smita relies on 2 types of foods F1 and F2. F1 provides 7, 5 and 2 units of A, B, C vitamins per 10 grams and F2 provides 2, 4 and 8 units of A, B and C vitamins per 10 grams. F1 costs ₹ 3 and F2 costs ₹ 2 per 10 grams. How many grams of each F1 and F2 should buy every day to keep her food bill minimum
A chemist has a compound to be made using 3 basic elements X, Y, Z so that it has at least 10 litres of X, 12 litres of Y and 20 litres of Z. He makes this compound by mixing two compounds (I) and (II). Each unit compound (I) had 4 litres of X, 3 litres of Y. Each unit compound (II) had 1 litre of X, 2 litres of Y and 4 litres of Z. The unit costs of compounds (I) and (II) are ₹ 400 and ₹ 600 respectively. Find the number of units of each compound to be produced so as to minimize the cost
Maximize Z = 5x + 10y subject to constraints
x + 2y ≤ 10, 3x + y ≤ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Minimize Z = 24x + 40y subject to constraints
6x + 8y ≥ 96, 7x + 12y ≥ 168, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Minimize Z = x + 4y subject to constraints
x + 3y ≥ 3, 2x + y ≥ 2, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Amartya wants to invest ₹ 45,000 in Indira Vikas Patra (IVP) and in Public Provident fund (PPF). He wants to invest at least ₹ 10,000 in PPF and at least ₹ 5000 in IVP. If the rate of interest on PPF is 8% per annum and that on IVP is 7% per annum. Formulate the above problem as LPP to determine maximum yearly income.
Solution: Let x be the amount (in ₹) invested in IVP and y be the amount (in ₹) invested in PPF.
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
As per the given condition, x + y ______ 45000
He wants to invest at least ₹ 10,000 in PPF.
∴ y ______ 10000
Amartya wants to invest at least ₹ 5000 in IVP.
∴ x ______ 5000
Total interest (Z) = ______
The formulated LPP is
Maximize Z = ______ subject to
______
Solve the following LPP graphically:
Maximize Z = 9x + 13y subject to constraints
2x + 3y ≤ 18, 2x + y ≤ 10, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solution: Convert the constraints into equations and find the intercept made by each one of it.
| Inequation | Equation | X intercept | Y intercept | Region |
| 2x + 3y ≤ 18 | 2x + 3y = 18 | (9, 0) | (0, ___) | Towards origin |
| 2x + y ≤ 10 | 2x + y = 10 | ( ___, 0) | (0, 10) | Towards origin |
| x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 | x = 0, y = 0 | X axis | Y axis | ______ |
The feasible region is OAPC, where O(0, 0), A(0, 6),
P( ___, ___ ), C(5, 0)
The optimal solution is in the following table:
| Point | Coordinates | Z = 9x + 13y | Values | Remark |
| O | (0, 0) | 9(0) + 13(0) | 0 | |
| A | (0, 6) | 9(0) + 13(6) | ______ | |
| P | ( ___,___ ) | 9( ___ ) + 13( ___ ) | ______ | ______ |
| C | (5, 0) | 9(5) + 13(0) | ______ |
∴ Z is maximum at __( ___, ___ ) with the value ___.
Solve the LPP graphically:
Minimize Z = 4x + 5y
Subject to the constraints 5x + y ≥ 10, x + y ≥ 6, x + 4y ≥ 12, x, y ≥ 0
Solution: Convert the constraints into equations and find the intercept made by each one of it.
| Inequations | Equations | X intercept | Y intercept | Region |
| 5x + y ≥ 10 | 5x + y = 10 | ( ___, 0) | (0, 10) | Away from origin |
| x + y ≥ 6 | x + y = 6 | (6, 0) | (0, ___ ) | Away from origin |
| x + 4y ≥ 12 | x + 4y = 12 | (12, 0) | (0, 3) | Away from origin |
| x, y ≥ 0 | x = 0, y = 0 | x = 0 | y = 0 | 1st quadrant |
∵ Origin has not satisfied the inequations.
∴ Solution of the inequations is away from origin.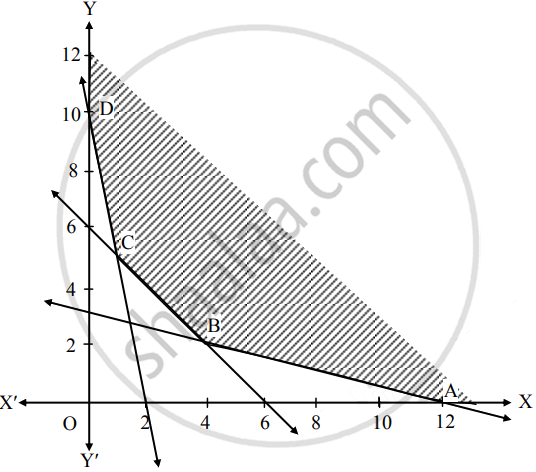
The feasible region is unbounded area which is satisfied by all constraints.
In the figure, ABCD represents
The set of the feasible solution where
A(12, 0), B( ___, ___ ), C ( ___, ___ ) and D(0, 10).
The coordinates of B are obtained by solving equations
x + 4y = 12 and x + y = 6
The coordinates of C are obtained by solving equations
5x + y = 10 and x + y = 6
Hence the optimum solution lies at the extreme points.
The optimal solution is in the following table:
| Point | Coordinates | Z = 4x + 5y | Values | Remark |
| A | (12, 0) | 4(12) + 5(0) | 48 | |
| B | ( ___, ___ ) | 4( ___) + 5(___ ) | ______ | ______ |
| C | ( ___, ___ ) | 4( ___) + 5(___ ) | ______ | |
| D | (0, 10) | 4(0) + 5(10) | 50 |
∴ Z is minimum at ___ ( ___, ___ ) with the value ___
A linear function z = ax + by, where a and b are constants, which has to be maximised or minimised according to a set of given condition is called a:-
Graphical solution set of the inequations x ≥ 0 and y ≤ 0 lies in ______ quadrant.
