Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A wire when bent in the form of a square encloses an area of 484 m2. Find the largest area enclosed by the same wire when bent to from:
- An equilateral triangle.
- A rectangle of length 16 m.
उत्तर
The area of the square is 484.
Let a be the length of each side of the square.
Now
a2 = 484
a = 22 m
Hence, the length of the wire is = 4 × 22 = 88 m.
(i) Now, this 88 m wire is bent in the form of an equilateral triangle.
Side of the triangle = `88/3`
= 29.3 m
Area of the triangle = `sqrt3/4` × (Side)2
= `sqrt3/4` × (29.3)2
= 372.58 m2
(ii) Let x be the breadth of the rectangle.
Now,
2(l + b) = 88
16 + x = 44
x = 28 m
Hence, area = 16 × 28 = 448 m2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The area of a parallelogram is y cm2 and its height is h cm. The base of another parallelogram is x cm more than the base of the first parallelogram and its area is twice the area of the first. Find, in terms of y, h, and x, the expression for the height of the second parallelogram.
A wire when bent in the form of a square encloses an area = 576 cm2. Find the largest area enclosed by the same wire when bent to form;
(i) an equilateral triangle.
(ii) A rectangle whose adjacent sides differ by 4 cm.
A rectangular plot of land measures 45 m x 30 m. A boundary wall of height 2.4 m is built all around the plot at a distance of 1 m from the plot. Find the area of the inner surface of the boundary wall.
Trapezium given below; find its area.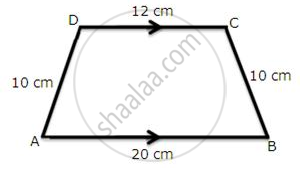
A footpath of uniform width runs all around the outside of a rectangular field 30 m long and 24 m wide. If the path occupies an area of 360 m2, find its width.
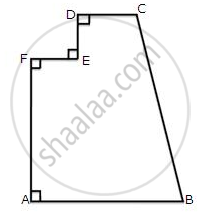
The figure given below shows the cross-section of a concrete structure. Calculate the area of cross-section if AB = 1.8 cm, CD = 0.6 m, DE = 0.8 m, EF = 0.3 m and AF = 1.2 m.
The perimeter of a rhombus is 46 cm. If the height of the rhombus is 8 cm; find its area.
The perimeter of a rhombus is 52 cm. If one diagonal is 24 cm; find:
(i) The length of its other diagonal,
(ii) Its area.
PQRS is a rectangle formed by joining the points P(– 1, – 1), Q(– 1, 4), R(5, 4) and S(5, – 1). A, B, C and D are the mid-points of PQ, QR, RS and SP respectively. Is the quadrilateral ABCD a square, a rectangle or a rhombus? Justify your answer.
If the diagonal d of a quadrilateral is doubled and the heights h1 and h2 falling on d are halved, then the area of quadrilateral is ______.
