Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
State and explain the law of demand.
उत्तर १
Law of Demand:-
The Law of demand is one of the important basic laws of consumption. Dr. Alfred Marshall, in his book "Principles of Economics", has explained the law of demand as follows.
"Other things being constant the higher the price of the commodity, smaller is the quantity demanded arid lower the Mice of the commodity larger is the quantity demanded."
The law of demand explains the change in the behaviour of consumer demand due to various changes in price. Marshall's Law of demand describes the functional relation between demand and price. It can be expressed as D = f (P) that is demand is a function of price. The relation between price and demand is inverse because the larger quantity is demanded when the price falls and a smaller quantity will be demanded when the price rises. The law of demand is explained with the help of the following schedule and diagram.
Table No. 3.3 = Demand Schedule
|
Price of Mangoes
Per Kg. (Rs.)
|
Demand for Mangoes
(Kg.)
|
| 50 | 1 |
| 40 | 2 |
| 30 | 3 |
| 20 | 4 |
| 10 | 5 |
As shown in the schedule when the price of mangoes is Rs. 5O/- per kg. demand is 1 kg. When the price falls to the level of Rs. 40/- per kg. and demand rises to 2 kg. Similarly, at the price of Rs. 10/- per kg. the demand for mangoes is 5 kg., whereas 4 kg. of mangoes are demanded at price Rs. 20/- per kg. This shows an inverse relation between price and demand.
In this diagram, X-axis represents demand for mangoes, whereas the Y" axis represents the price of mangoes. DD is demand! the curve which slopes downwards from left to right. In other words, its slope is negative because of the inverse relationship between price and demand.
उत्तर २
The law of demand focuses on the basic relationship between the price of the goods and quantity demanded of the good.
According to this law, other things being constant (ceteris paribus), a consumer’s demand shares an inverse relationship with the price of a good and vice versa. In other words, if the income, price of related goods, and taste and preferences of the consumer remain unchanged, then the demand for the good moves in the opposite direction of its price.
उत्तर ३
According to the law of demand, a consumer’s demand shares an inverse relationship with the price of a good and vice-versa, ceteris paribus (other things being constant). In other words, if the income, price of related goods and a consumer’s tastes and preferences remain unchanged, then the demand of a good move opposite to the movement in the price of those goods.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain, with reasons, whether you Agree or Disagree with the following statement
There are no exceptions to the Law of Demand.
Demand for perishable goods is inelastic.
Demand curve and Supply curve.
Define demand. Name the factors affecting market demand.
Compare inelastic demand with perfectly inelastic demand.
The demand of a commodity, when measured through the expenditure approach, is inelastic. A fall in its price will result in : (choose the correct alternative)
(a) No change in expenditure on it.
(b) Increase in expenditure on it.
(c) Decrease in expenditure on it.
(d) Anyone of the above.
Demand deposits include (choose the correct alternative)
(a) Saving account deposits and fixed deposits
(b) Saving account deposits and current account deposits
(c) Current account deposits and fixed deposits
(d) All types of deposits
When the income of the consumer falls the impact on a price-demand curve of an inferior good is: (choose the correct alternative)
a. Shifts to the right.
b. Shifts of the left.
c. There is upward movement along the curve.
d. There is downward movement along the curve
If due to fall in the price of good X, demand for good Y rises, the two goods are : (Choose the correct alternative)
a. Substitutes
b. Complements
c. Not related
d. Competitive
When is demand called perfectly inelastic?
Demand for electricity is elastic.
Give reason or Explain the following statement :
Demand for habitually used goods is inelastic.
Define or explain the following concept :
Effective demand .
Fill in the blank using proper alternative given in the bracket:
Perfectly inelastic demand curve is.....................................................
State with reason. Whether you ‘agree’ or ‘disagree’ with the following statement:
There are no exceptions to the law of Demand.
State whether the following statement is true or false.
Perfectly inelastic demand curve is parallel to ‘X’ axis.
Fill in the blanks using proper alternatives given in the brackets.
Demand for car and petrol is ____________ de
Write whether the following statement is True or False:
Demand curve has a positive slope.
(b) less elastic demand
(c) zero elastic demand
(d) unitary elastic demand
Distinguish between :
Individual demand schedule and Market demand schedule.
Write Explanatory answer.
State and explain the law of demand with its exception.
fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given in the bracket:
Demand for salt is ___________.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given below:
When less is purchased at the constant price, it is called _______ in demand.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given below:
Market demand is an aggregate of purchasing by _________ buyers.
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE
Demand curve slopes upward from left to right.
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE
When demand increases, the demand curve shifts to the left.
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE
Individual demand is a demand by single buyer.
Define or explain the following concept:
Derived demand
Define or explain the following concept:
Direct demand
Give reason or explain the following statement.
Increase in demand indicates a rightward shift in the demand curve.
Give reason or explain the following statement.
Demand curve slopes downward from left to right.
Give reason or explain the following statement.
Demand for factors of production is derived demand.
Distinguish between Desire and Demand.
Answer the following question.
Discuss the relationship between the income of the consumer and demand for a commodity with respect to normal goods, inferior goods, and necessities.
Distinguish between substitute goods and complementary goods, with examples.
Distinguish between normal goods and inferior goods, with examples
State whether the following statement is true or false. Give reasons for your answer :
X and Y are complementary goods. A fall in the price of Y will result in a rise in the price of X.
Answer the following question:
Elaborate the law of demand, with the help of a hypothetical schedule.
If the price of good X rises and it leads to an increase in demand for good Y, both are ______ goods.
We say that there is a decrease in demand when ______
There is a sudden change in climatic conditions resulting in hot weather. Assuming no change in the price of the cold drinks, it will lead to ______
Law of demand states the ______ relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Which of the following points are related to the 'Paradox of Thrift'?
Increase in price of substitute goods leads to ______
From the set of statements given in Column A and Column B, choose the correct pair of statement:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Reduction of pollution | (a) Microeconomics |
| 2. Problems due to unemployment | (b) Microeconomics |
| 3. Shift in the demand curve | (c) Microeconomics |
| 4. Government expenditure on building of roads | (d) Microeconomics |
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Utility | (a) Bread and butter |
| (2) Normal Goods | (b) Rise in price |
| (3) Contraction in demand | (c) Capacity of a commodity to satisfy human wants. |
| (4) Complementary goods | (d) Positively related |
Identify the two cost curves which start from the same point on the Y-axis.
Which of the following is correct?
Read the following news report and answer the Q.97-Q.100 on the basis of the same:
The quantity of a commodity that a consumer is willing to buy and is able to afford, given the prices of goods and the consumer's tastes and preferences is called demand for the commodity. Whenever one or more of these variables change, the quantity of the good Chosen by the consumer is likely to change as well. The relation between the consumer's optimal choice of the quantity of a good and its price is very important and this relation is called the demand function. Thus, the consumer's demand function for a good gives the amount of the good that the consumer chooses at different levels of its price when the other things remain.
In which of the following cases there will be leftward shift in demand?
Read the following news report and answer the Q.97-Q.100 on the basis of the same:
The quantity of a commodity that a consumer is willing to buy and is able to afford, given the prices of goods and the consumer's tastes and preferences is called demand for the commodity. Whenever one or more of these variables change, the quantity of the good Chosen by the consumer is likely to change as well. The relation between the consumer's optimal choice of the quantity of a good and its price is very important and this relation is called the demand function. Thus, the consumer's demand function for a good gives the amount of the good that the consumer chooses at different levels of its price when the other things remain.
What is meant by the contraction of demand?
Which of the following statement is true?
Which of the following is the reason behind the downward slope of demand option?
When the price of the commodity has changed the demand for the commodity changes in ______
Which of the following statements is true?
In an open economy, Aggregate Demand is estimated as:
Identify the correctly matched pair of the items in Column A to that of Column B.
| Column A | Column B | ||
| (1) | Increase in demand for goods | (a) | Leftward shift in the demand curve |
| (2) | Decrease in demand | (b) | Perfectly Elastic Demand |
| (3) | Ed = ∞ | (c) | Increases in the income of the consumer |
| (4) | Downward Sloping | (d) | Income elasticity of Demand |
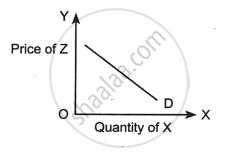
The figure given below shows the relation between the quantity demanded for the good X and the price of the good Z. What type of goods are X and Z?
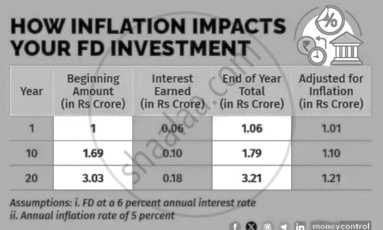
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow.
|
In India, Fixed deposits have long been a favourite investment choice of people, especially senior citizens, as it promise steady returns. It attracts those who are seeking a stable income. But it’s an illusion in the period of inflation. Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, subsequently eroding the purchasing power of money. In simple terms, what money could buy today might not a few years down the line. Fixed deposits are financial instruments offered by banks where you deposit a lump sum amount for a fixed period at a predetermined rate of interest. Consider an investment of Rs 1 crore in a fixed deposit at a 6% annual interest rate and the annual rate of inflation is 5%. By the 10th year your pre inflation return is 1.79 crore, but post inflation it’s just 1.10 crore. The nominal value of investment in fixed deposits may appear to grow, inflation significantly diminishes their real value and purchasing power over time.
|
- What is the theme of the extract? (2)
- Differentiate between Demand pull and Cost push inflation. (2)
- What are the demand deposits and time deposits? (2)
- Since 1998 RBI has been using new measures of money supply, M0, M1, M2 and M3. Which one of these measures incorporates fixed deposit as one of its components? Mention the other components of that measure. (2)