Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Can the potential difference across a battery be greater than its emf?
उत्तर
The potential difference across a battery can be greater than its emf. When the battery is being charged. Basically, emf is the maximum potential difference between the terminals of a battery when the terminals are not connected externally to an electric circuit. Current flows in the closed circuit when the same battery is connected to an electric circuit. When current flows, the potential difference across the terminals of the battery is decreased as some potential drop due to its internal resistance.
Due to the internal resistance in the battery, the potential difference across it is less than its emf. However, for an ideal battery, potential difference and emf are equal.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between emf and terminal voltage of a cell.
A cell of emf 'E' and internal resistance 'r' is connected across a variable load resistor R. Draw the plots of the terminal voltage V versus (i) R and (ii) the current I.
It is found that when R = 4 Ω, the current is 1 A and when R is increased to 9 Ω, the current reduces to 0.5 A. Find the values of the emf E and internal resistance r.
A storage battery of emf 8.0 V and internal resistance 0.5 Ω is being charged by a 120 V dc supply using a series resistor of 15.5 Ω. What is the terminal voltage of the battery during charging? What is the purpose of having a series resistor in the charging circuit?
Nichrome and copper wires of same length and same radius are connected in series. Current I is passed through them. Which wire gets heated up more? Justify your answer.
A resistor R is connected to a cell of-emf e and internal resistance r. The potential difference across the resistor R is found to be V. State the relation between e, V, Rand r.
Plot a graph showing variation of voltage vs the current drawn from the cell. How can one get information from this plot about the emf of the cell and its internal resistance?
Two identical cells, each of emf E, having negligible internal resistance, are connected in parallel with each other across an external resistance R. What is the current through this resistance?
A cell of emf ‘E’ and internal resistance ‘r’ is connected across a variable resistor ‘R’. Plot a graph showing the variation of terminal potential ‘V’ with resistance R. Predict from the graph the condition under which ‘V’ becomes equal to ‘E’.
Two non-ideal batteries are connected in parallel. Consider the following statements:-
(A) The equivalent emf is smaller than either of the two emfs.
(B) The equivalent internal resistance is smaller than either of the two internal resistances.
A battery of emf 100 V and a resistor of resistance 10 kΩ are joined in series. This system is used as a source to supply current to an external resistance R. If R is not greater than 100 Ω, the current through it is constant up to two significant digits.
Find its value. This is the basic principle of a constant-current source.
Find the equivalent resistance of the network shown in the figure between the points a and b.
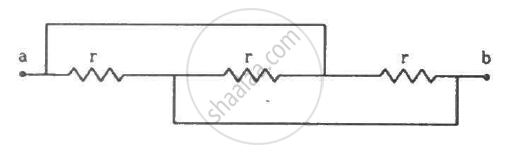
Apply the first law of thermodynamics to a resistor carrying a current i. Identify which of the quantities ∆Q, ∆U and ∆W are zero, positive and negative.
Do the electrodes in an electrolytic cell have fixed polarity like a battery?
Find the emf of the battery shown in the figure:
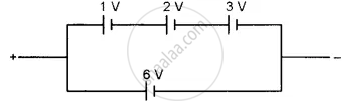
Answer the following question.
A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a variable resistor R. Plot the shape of graphs showing a variation of terminal voltage V with (i) R and (ii) circuit current I.
The internal resistance of a cell is the resistance of ______
Two batteries of emf ε1 and ε2 (ε2 > ε1) and internal resistances r1 and r2 respectively are connected in parallel as shown in figure.
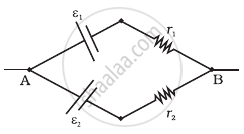
A battery of EMF 10V sets up a current of 1A when connected across a resistor of 8Ω. If the resistor is shunted by another 8Ω resistor, what would be the current in the circuit? (in A)
