Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
|
Case Study Trigonometry in the form of triangulation forms the basis of navigation, whether it is by land, sea or air. GPS a radio navigation system helps to locate our position on earth with the help of satellites. |
- Make a labelled figure on the basis of the given information and calculate the distance of the boat from the foot of the observation tower.
- After 10 minutes, the guard observed that the boat was approaching the tower and its distance from tower is reduced by 240(`sqrt(3)` - 1) m. He immediately raised the alarm. What was the new angle of depression of the boat from the top of the observation tower?
उत्तर
i.
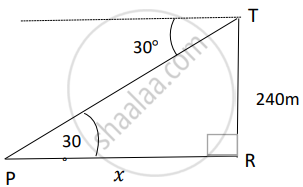
In ∆PTR, tan 30° = `240/x` ⇒ x = `240sqrt(3)` m
ii. Distance of boat from tower = `240sqrt(3) - 240(sqrt(3) - 1)` = 240 m
Let the angle of depression = θ
tan θ = `240/240` = 1 ⇒ θ = 45°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The x-coordinate of a point P is twice its y-coordinate. If P is equidistant from Q(2, –5) and R(–3, 6), find the coordinates of P.
Find the coordinates of the centre of the circle passing through the points (0, 0), (–2, 1) and (–3, 2). Also, find its radius.
If Q (0, 1) is equidistant from P (5, − 3) and R (x, 6), find the values of x. Also find the distance QR and PR.
Show that the quadrilateral whose vertices are (2, −1), (3, 4) (−2, 3) and (−3,−2) is a rhombus.
Find the point on the x-axis equidistant from the points (5,4) and (-2,3).
Find the coordinate of O , the centre of a circle passing through P (3 , 0), Q (2 , `sqrt 5`) and R (`-2 sqrt 2` , -1). Also find its radius.
The centre of a circle passing through P(8, 5) is (x+l , x-4). Find the coordinates of the centre if the diameter of the circle is 20 units.
Show that the quadrilateral with vertices (3, 2), (0, 5), (- 3, 2) and (0, -1) is a square.
The distance between the points A(0, 6) and B(0, –2) is ______.
|
In a GPS, The lines that run east-west are known as lines of latitude, and the lines running north-south are known as lines of longitude. The latitude and the longitude of a place are its coordinates and the distance formula is used to find the distance between two places. The distance between two parallel lines is approximately 150 km. A family from Uttar Pradesh planned a round trip from Lucknow (L) to Puri (P) via Bhuj (B) and Nashik (N) as shown in the given figure below.
|
Based on the above information answer the following questions using the coordinate geometry.
- Find the distance between Lucknow (L) to Bhuj (B).
- If Kota (K), internally divide the line segment joining Lucknow (L) to Bhuj (B) into 3 : 2 then find the coordinate of Kota (K).
- Name the type of triangle formed by the places Lucknow (L), Nashik (N) and Puri (P)
[OR]
Find a place (point) on the longitude (y-axis) which is equidistant from the points Lucknow (L) and Puri (P).


