Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Choose the correct option.
Consider the following cases:
(P) A planet revolving in an elliptical orbit.
(Q) A planet revolving in a circular orbit.
Principle of conservation of angular momentum comes in force in which of these?
पर्याय
Only for (P)
Only for (Q)
For both, (P) and (Q)
Neither for (P), nor for (Q)
उत्तर
For both, (P) and (Q)
Explanation:
The following cases,
- Angular momentum is conserved for any rotating motion rather elliptical or circular.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A stone of mass 0.25 kg tied to the end of a string is whirled round in a circle of radius 1.5 m with a speed of 40 rev/min in a horizontal plane. What is the tension in the string? What is the maximum speed with which the stone can be whirled around if the string can withstand a maximum tension of 200 N?
When a particle moves in a circle with a uniform speed
Tow cars having masses m1 and m2 moves in circles of radii r1 and r2 respectively. If they complete the circle in equal time, the ratio of their angular speed ω1/ω2 is
Water in a bucket is whirled in a vertical circle with string attached to it. The water does no fall down even when the bucket is inverted at the top of its path. We conclude that in this position
A stone of mass m tied to a string of length l is rotated in a circle with the other end of the string as the centre. The speed of the stone is v. If the string breaks, the stone will move
A coin placed on a rotating turntable just slips. If it is placed at a distance of 4 cm from the centre. If the angular velocity of the turntable is doubled, it will just slip at a distance of
A motorcycle is going on an overbridge of radius R. The driver maintains a constant speed. As the motorcycle is ascending on the overbridge, the normal force on it
Three identical cars A, B and C are moving at the same speed on three bridges. The car A goes on a place bridge, B on a bridge convex upward and C goes on a bridge concave upward. Let FA, FB and FC be the normal forces exerted by the car on the bridges when they are at the middle of bridges.
An object follows a curved path. The following quantities may remain constant during the motion
(a) speed
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) magnitude of acceleration.
Find the acceleration of the moon with respect to the earth from the following data:
Distance between the earth and the moon = 3.85 × 105 km and the time taken by the moon to complete one revolution around the earth = 27.3 days.
A mosquito is sitting on an L.P. record disc rotating on a turn table at \[33\frac{1}{3}\] revolutions per minute. The distance of the mosquito from the centre of the turn table is 10 cm. Show that the friction coefficient between the record and the mosquito is greater than π2/81. Take g =10 m/s2.
Suppose the bob of the previous problem has a speed of 1.4 m/s when the string makes an angle of 0.20 radian with the vertical. Find the tension at this instant. You can use cos θ ≈ 1 − θ2/2 and SINθ ≈ θ for small θ.
Suppose the amplitude of a simple pendulum having a bob of mass m is θ0. Find the tension in the string when the bob is at its extreme position.
A track consists of two circular parts ABC and CDE of equal radius 100 m and joined smoothly as shown in figure. Each part subtends a right angle at its centre. A cycle weighing 100 kg together with the rider travels at a constant speed of 18 km/h on the track. (a) Find the normal contact force by the road on the cycle when it is at B and at D. (b) Find the force of friction exerted by the track on the tyres when the cycle is at B, C and. (c) Find the normal force between the road and the cycle just before and just after the cycle crosses C. (d) What should be the minimum friction coefficient between the road and the tyre, which will ensure that the cyclist can move with constant speed? Take g = 10 m/s2.
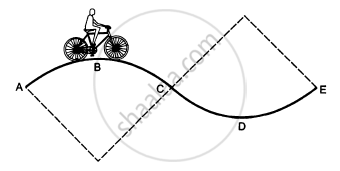
What is the radius of curvature of the parabola traced out by the projectile in the previous problem at a point where the particle velocity makes an angle θ/2 with the horizontal?
A particle of mass 1 kg, tied to a 1.2 m long string is whirled to perform the vertical circular motion, under gravity. The minimum speed of a particle is 5 m/s. Consider the following statements.
P) Maximum speed must be `5sqrt5` m/s.
Q) Difference between maximum and minimum tensions along the string is 60 N.
Select the correct option.
In non-uniform circular motion, the ratio of tangential to radial acceleration is (r = radius, a = angular acceleration and v = linear velocity)
A body slides down a smooth inclined plane having angle θ and reaches the bottom with velocity v. If a body is a sphere, then its linear velocity at the bottom of the plane is
A particle of mass m is performing UCM along a circle of radius r. The relation between centripetal acceleration a and kinetic energy E is given by
A particle is moving in a radius R with constant speed v. The magnitude of average acceleration after half revolution is ____________.
A rope is wound around a solid cylinder of mass 1 kg and radius 0.4 m. What is the angular acceleration of cylinder, if the rope is pulled with a force of 25 N? (Cylinder is rotating about its own axis.)
The real force 'F' acting on a particle of mass ' m' performing circular motion acts along the radius of circle 'r' and is directed towards the centre of circle. The square root of the magnitude of such force is (T = periodic time).
A body of M.I. 2 kg m2 rotates with an angular velocity of 20 rad/s. When an external torque of 0.5 N m acts on it in the opposite direction, the number of revolutions it makes before it comes to rest is ____________.
A person driving a car suddenly applies the brakes on seeing a child on the road ahead. If he is not wearing seat belt, he falls forward and hits his head against the steering wheel. Why?
A block of 200 g mass moves with a uniform speed in a horizontal circular groove, with vertical side walls of radius 20 cm. If the block takes 40 s to complete one round, the normal force by the side walls of the groove is ______.
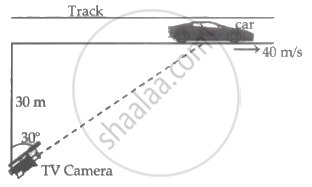
A racing car is travelling along a track at a constant speed of 40 m/s. A T.V. cameraman is recording the event from a distance of 30 m directly away from the track as shown in the figure. In order to keep the car under view in the position shown, the angular speed with which the camera should be rotated is ______.
Which of the following statements is FALSE for a particle moving in a circle with a constant angular speed?
