Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Construct a Δ XYZ in which XY= 4 cm, YZ = 5 cm and ∠ Y = 1200. Locate a point T such that ∠ YXT is a right angle and Tis equidistant from Y and Z. Measure TZ.
उत्तर
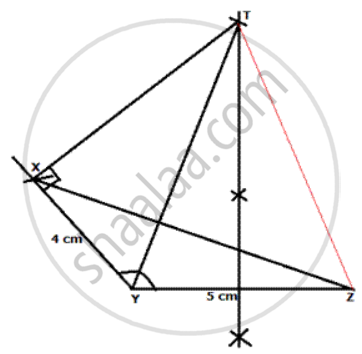
Steps of Construction:
(i) Draw YZ = 5 cm
(ii) Draw an arc with angle Y= 120 ° and radius 4 cm.
(iii) Join XZ.
(iv) Draw perpendicular bisector of YZ.
(v) With X as centre and angle X as 90° , join X to the perpendicular bisectcr at T. T is the required point.
(vi) Measure TY. TY = 6.8 cm = TZ as T lies on perpendicular bisector of YZ.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Angle ABC = 60° and BA = BC = 8 cm. The mid-points of BA and BC are M and N respectively. Draw and describe the locus of a point which is:
- equidistant from BA and BC.
- 4 cm from M.
- 4 cm from N.
Mark the point P, which is 4 cm from both M and N, and equidistant from BA and BC. Join MP and NP, and describe the figure BMPN.
Construct a triangle ABC, with AB = 6 cm, AC = BC = 9 cm. Find a point 4 cm from A and equidistant from B and C.
Two straight roads AB and CD cross each other at Pat an angle of 75° . X is a stone on the road AB, 800m from P towards B. BY taking an appropriate scale draw a figure to locate the position of a pole, which is equidistant from P and X, and is also equidistant from the roads.
Draw and describe the lorus in the following cases:
The Iocus of the mid-points of all parallel chords of a circle.
Draw and describe the lorus in the following cases:
The lorus of a point in rhombus ABCD which is equidistant from AB and AD .
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Point in a plane equidistant from a given line.
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Centre of a circle of varying radius and touching the two arms of ∠ ABC.
Without using set squares or protractor construct a triangle ABC in which AB = 4 cm, BC = 5 cm and ∠ABC = 120°.
(i) Locate the point P such that ∠BAp = 90° and BP = CP.
(ii) Measure the length of BP.
Using ruler and compasses construct:
(i) a triangle ABC in which AB = 5.5 cm, BC = 3.4 cm and CA = 4.9 cm.
(ii) the locus of point equidistant from A and C.
(iii) a circle touching AB at A and passing through C.
Use ruler and compasses only for the following questions:
Construct triangle BCP, when CB = 5 cm, BP = 4 cm, ∠PBC = 45°.
Complete the rectangle ABCD such that :
(i) P is equidistant from AB and BC and
(ii) P is equidistant from C and D. Measure and write down the length of AB.
