Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
D is any point on side AC of a ∆ABC with AB = AC. Show that CD < BD.
उत्तर
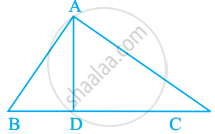
Given in triangle ABC, D is any point on side AC such that AB = AC.
To proof that CD < BD or BD > CD
To proof: AC = AB ...[Given]
∠ABC = ∠ACB ...(i) [Angle opposite to equal sides are equal]
In triangle ABC and triangle DBC,
∠ABC > ∠DBC ...[∠DBC is a internal angle of ∠B]
∠ACB > ∠DBC ...[From equation (i)]
BD > CD ...[Side opposite to greater angle is longer]
CD < BD
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blank to make the following statement true:
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the two ....... opposite angles.
The sum of two angles of a triangle is equal to its third angle. Determine the measure of the third angle.
If the side BC of ΔABC is produced on both sides, then write the difference between the sum of the exterior angles so formed and ∠A.
In a triangle ABC, ∠A = 45° and ∠B = 75°, find ∠C.
In the given figure, show that: ∠a = ∠b + ∠c
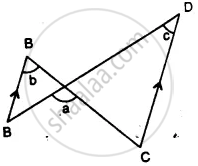
(i) If ∠b = 60° and ∠c = 50° ; find ∠a.
(ii) If ∠a = 100° and ∠b = 55° : find ∠c.
(iii) If ∠a = 108° and ∠c = 48° ; find ∠b.
Can a triangle together have the following angles?
33°, 74° and 73°
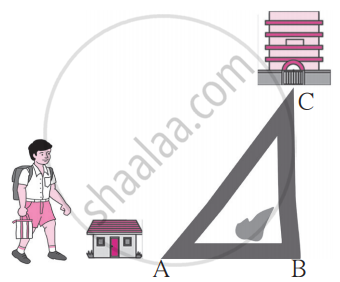
As shown in the figure, Avinash is standing near his house. He can choose from two roads to go to school. Which way is shorter? Explain why.
Bisectors of the angles B and C of an isosceles triangle with AB = AC intersect each other at O. BO is produced to a point M. Prove that ∠MOC = ∠ABC.
The number of triangles in figure is ______.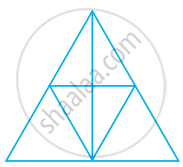
In figure, ∠BAC = 90° and AD ⊥ BC. The number of right triangles in the figure is ______.