Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
S is any point on side QR of a ∆PQR. Show that: PQ + QR + RP > 2PS.
उत्तर
Given: In ∆PQR, S is any point on side QR.
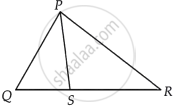
To show: PQ + QR + RP > 2PS
Proof: In ∆PQS,
PQ + QS > PS ...(i) [Sum of two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side]
Similarly, in ∆PRS,
SR + RP > PS ...(ii) [Sum of two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side]
On adding equations (i) and (ii), we get
PQ + QS + SR + RP > 2PS
⇒ PQ + (QS + SR) + RP > 2PS
⇒ PQ + QR + RP > 2PS ...[∵ QR = QS + SR]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Is the following statement true and false :
A triangle can have two obtuse angles.
If two acute angles of a right triangle are equal, then each acute is equal to
Find the unknown marked angles in the given figure:

Calculate the angles of a triangle if they are in the ratio 4: 5: 6.
Find x, if the angles of a triangle is:
2x°, 4x°, 6x°
One angle of a right-angled triangle is 70°. Find the other acute angle.
Classify the following triangle according to sides:
The length of the three segments is given for constructing a triangle. Say whether a triangle with these sides can be drawn. Give the reason for your answer.
9 cm, 6 cm, 16 cm
The length of the three segments is given for constructing a triangle. Say whether a triangle with these sides can be drawn. Give the reason for your answer.
15 cm, 20 cm, 25 cm
Can you draw a triangle with 25°, 65° and 80° as angles?
