Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw an inscribing circle of a regular hexagon of side 5.8 cm.
उत्तर
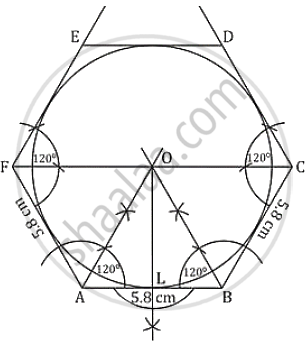
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment AB = 5.8 cm.
- At A and B, draw rays making an angle of 120° each and cut off AF = BC = 5.8 cm.
- Again F and C, draw rays making an angle of 120° each and cut off FE = CD = 5.8 cm.
- Join DE. Then ABCDEF is the regular hexagon.
- Draw the bisectors of ∠A and ∠B intersecting each other at O.
- From O, draw OL ⊥ AB.
- With centre O and radius OL, draw a circle which touches the sides of the hexagon.
This is the required in circle of the hexagon.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Construct a tangent to a circle of radius 4 cm from a point on the concentric circle of radius 6 cm and measure its length. Also verify the measurement by actual calculation.
In the figure given below, diameter AB and chord CD of a circle meet at P. PT is a tangent to the circle at T. CD = 7.8 cm, PD = 5 cm, PB = 4 cm. Find:
1) AB.
2) the length of tangent PT.

Using ruler and compasses only construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 4 cm, ∠ACB = 45° and perpendicular from A on BC is 2.5 cm. Draw a circle circumscribing the triangle ABC and measure its radius.
The bisectors of angles A and B of a scalene triangle ABC meet at O.
- What is the point O called?
- OR and OQ are drawn perpendicular to AB and CA respectively. What is the relation between OR and OQ?
- What is the relation between angle ACO and angle BCO?
Draw a circle of radius 3.5 cm. Take two points A and B on one of its extended diameter, each at a distance of 5 cm from its center. Draw tangents to the circle from each of these points A and B.
Draw a circle with center O and radius 4 cm. Draw any diameter AB of this circle. Construct tangents to the circle at each of the two end points of the diameter AB.
Draw a pair of tangents to a circle of radius 3 cm, which are inclined to each other at an angle of 60°.
Draw two concentric circles with radii 4 cm and 6 cm. Taking a point on the outer circle, construct a pair of tangents to inner circle. By measuring the lengths of both the tangents, show that they are equal to each other.
Construct a tangent to a circle of radius 4 cm from a point which is at a distance of 6 cm from its centre.
Draw two concentric circles of radii 3 cm and 5 cm. Taking a point on outer circle construct the pair of tangents to the other. Measure the length of a tangent and verify it by actual calculation.
