Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the terms Corrosion
Explain the term "corrosion" with an example.
उत्तर १
Corrosion is defined as a process where materials, usually metals, deteriorate as a result of a chemical reaction with air, moisture, chemicals, etc. For example, in the presence of moisture, iron reacts with oxygen to form hydrated iron oxide.
\[\ce{4Fe + 3O2 + H2O → 2Fe2O3.nH2O}\]
उत्तर २
Corrosion is a process where a refined metal is oxidised by atmospheric oxygen to form a more stable compound, such as oxides. The metal gradually degrades during the corrosion process. Iron rusting is a good example of corrosion, where the iron is converted to iron oxide. Millions of dollars are spent annually to prevent rusting on bridges and other monuments.
उत्तर ३
Corrosion is the process by which metal corrodes when it comes into contact with its surroundings, such as moisture, air, and acids. For example, a powdered (brown) coating on iron objects such as iron railings.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Tinning : Tin : : Galvanizing : _________
Which metals do not corrode easily?
Explain why Iron sheets are coated with zinc during galvanization.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Heating an ore in a limited supply of air or in the absence of air at a temperature just below its melting point is known as
A. Smelting
B. Ore-dressing
C. Calcination
D. Bessemerisation
The chemical reaction involved in the corrosion of iron metal is that of:
(a) oxidation as well as displacement
(b) reduction as well as combination
(c) oxidation as well as combination
(d) reduction as well as displacement
What is meant by galvanisation? Why is it done?
Name the metal which is used for galvanising iron.
State two conditions for the rusting of iron.
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words:
............ and .............. are necessary for the rusting of iron.
Brass is an alloy of:
(a) Cu and Sn
(b) Cu and Pb
(c) Pb and Sn
(d) Zn and Cu
No chemical reaction takes place when granules of a rusty-brown solid A are mixed with the powder of another solid B. However, when the mixture is heated, a reaction takes place between its components. One of the products C is a metal and settles down in the molten state while the other product D floats over it. It was observed that the reaction is highly exothermic.
(a) What could the solids A and B be?
(b) What are the products C and D most likely to be?
(c) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between A and B leading to the formation of C and D. Mention the physical states of all the reactants and products in this equation and indicate the heat change which takes place.
(d) What is the special name of such a reaction? State one use of such a reaction.
(e) Name any two types of chemical reactions under which the above reaction can be classified.
Four metals P, Q, R and S are all obtained by the reduction of their oxides with carbon. Metal P is used to form a thin layer over the sheets of metal S to prevent its corrosion. Metal Q is used for electroplating tiffin boxes made of metal S whereas metal R is used in making car batteries. Metals Q and R form an alloy called solder. What are metals P, Q, R and S? How have you arrived at this conclusion?
Explain how the activity series accounts for each of the following:
tendency to corrosion
Corrosion can be an advantage in some case.Explain ?
No chemical reaction takes place when granules of a solid, A, are mixed with the powder of another solid, B. However when the mixture is heated, a reaction takes place between its components. One of the products, C, is a metal and settles down in the molten state while the other product, D, floats over it. It was observed that the reaction is highly exothermic.
(i) Based on the given information make an assumption about A and B and write a chemical equation for the chemical reaction indicating the conditions of reaction, physical state of reactants and products and thermal status of reaction.
(ii) Mention any two types of reactions under which above chemical reaction can be classified.
Answer the following question.
a) What is meant by corrosion?
b) Write names of any two methods of prevention of corrosion.
c) In which method, metal like copper, aluminium are coated with a thin layer of their oxides by means of electrolysis.
d) Explain this method with diagram.
Find the odd man out:
What is done to prevent corrosion of metals?
What are the adverse effects of corrosion?
Give reason.
An iron article should be given a coat of paint
Give reason.
A wooden article should be polished.
Observe the following picture and answer the following questions:

- What is rust?
- Write the chemical formula of rust.
- Write the reaction of oxidation of iron at the anode.
- Write the reaction of oxidation of iron at the cathode.
- What is corrosion?
_______ forms a green colour in the water.
When one of the metals in an alloy is mercury the alloy is called _______.
Write the name.
An alloy of copper and tin-
Write the name.
Method used to prevent corrosion of copper.
Write scientific reason.
On exposure to air, silver articles turn blackish after some time.
What is rust?
Observe the following diagram and give answers.
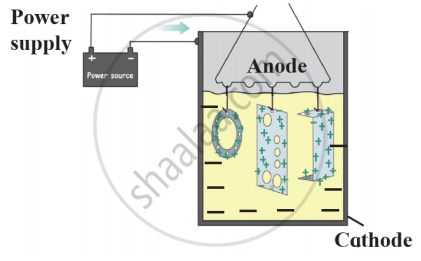
- Name this method of prevention of corrosion.
- For prevention of which metal this method is used?
- What is used as anode in this method?
State two conditions necessary for rusting of iron.
Galvanisation is a method of protecting iron from rusting by coating it with a thin layer of ____________.
The table shown below gives information about four substances: A, B, C and D.
| SUBSTANCE | MELTING POINT (K) | ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY | |
| SOLID | LIQUID/ AQUEOUS | ||
| A | 295 | Good | Good |
| B | 1210 | Poor | Good |
| C | 1890 | Poor | Good |
| D | 1160 | Poor | Poor |
Identify Ionic compounds from the above given substances.
Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of a metal with a metal or nonmetal. Which among the following alloys contain non-metal as one of its constituents?
Explain the following:
Lime water turns milky on passing carbon dioxide gas into it.
Give an example of a chemical reaction for each of the following situations:
Sound is produced
Give scientific reasons.
Silver amalgam is used for filling dental cavities.
Explain the chemical reactions in rusting of iron.
In ______ process a layer of molten tin is deposited on metals.
