Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the magnetic field due to a long straight conductor using Ampere’s circuital law.
उत्तर
Consider a straight conductor of infinite length carrying current I and the direction of magnetic field lines. Since the wire is geometrically cylindrical in shape C and symmetrical about its axis, we construct an Amperian loop in the form of a circular shape at a distance r from the centre of the conductor. From the Ampere’s law, we get
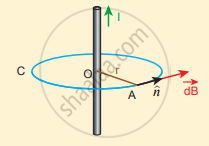
Ampèrian loop for current carrying straight wire
`oint_"C" vec"B"*"d"vec"l" = mu_0 "I"`
Where dl is the line element along the amperian loop (tangent to the circular loop). Hence, the angle between the magnetic field vector and line element is zero. Therefore,
`oint_"C" "B"*"dl" = mu_0 "I"`
where I is the current enclosed by the Amperian loop. Due to the symmetry, the magnitude of the magnetic field is uniform over the Amperian loop, we can take B out of the integration.
`"B"oint_"C" "dl" = mu_0"I"`
For a circular loop, the circumference is 2πr, which implies,
`"B"int_hat"n"^(2pi"r") "dl" = mu_0 "I"`
`vec"B"*2pi"r" = mmu_0"I"`
`=> vec"B" = (mu_0"I")/(2pi"r")`
In vector form, the magnetic field is
`vec"B" = (mu_0"I")/(2pi"r")hat"n"`
Where `hat"n"` is the unit vector along the tangent to the Amperian loop. This perfectly agrees with the result obtained from Biot-Savarf s law as given in equation
`vec"B" = (mu_0"I")/(2pi"a") hat"n"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Electron drift speed is estimated to be of the order of mm s−1. Yet large current of the order of few amperes can be set up in the wire. Explain briefly.
Obtain an expression for magnetic induction along the axis of the toroid.
Consider the situation described in the previous problem. Suppose the current i enters the loop at the points A and leaves it at the point B. Find the magnetic field at the centre of the loop.
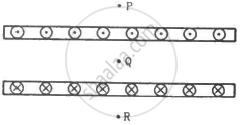
Two large metal sheets carry currents as shown in figure. The current through a strip of width dl is Kdl where K is a constant. Find the magnetic field at the points P, Q and R.
Define ampere.
The force required to double the length of a steel wire of area 1 cm2, if it's Young's modulus Y = `2 xx 10^11/m^2` is:
Ampere's circuital law is used to find out ______
When current flowing through a solenoid decreases from 5A to 0 in 20 milliseconds, an emf of 500V is induced in it.
- What is this phenomenon called?
- Calculate coefficient of self-inductance of the solenoid.
