Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given the moment of inertia of a disc of mass M and radius R about any of its diameters to be MR2/4, find its moment of inertia about an axis normal to the disc and passing through a point on its edge
उत्तर १
`3/2 MR^2`
The moment of inertia of disc about its diameter = `1/4 MR^2`
According to the theorem of the perpendicular axis, the moment of inertia of a planar body (lamina) about an axis perpendicular to its plane is equal to the sum of its moments of inertia about two perpendicular axes concurrent with the perpendicular axis and lying in the plane of the body.
The M.I of the disc about its centre =` 1/4 MR^2 + 1/4MR^2 = 1/2MR^2`
The situation is shown in the given figure
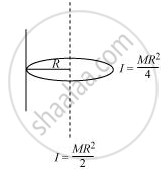
Applying the theorem of parallel axes:
The moment of inertia about an axis normal to the disc and passing through a point on its edge
`= 1/2 MR^2 + MR^2 = 3/2 MR^2`
उत्तर २
We are given, moment of inertia of the disc about any of its diameters = 1/4 MR2
(i) Using theorem of perpendicular axes, moment of inertia of the disc about an axis passing through its centre and normal to the disc = 2 x 1/4 MR2 = 1/2 MR2
(ii) Using theorem axes, moment of inertia of the disc passing through a point on its edge and normal to the dies = 1/2 MR2+ MR2 = 3/2 MR2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rope of negligible mass is wound round a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N? What is the linear acceleration of the rope? Assume that there is no slipping.
The oxygen molecule has a mass of 5.30 × 10–26 kg and a moment of inertia of 1.94×10–46 kg m2 about an axis through its centre perpendicular to the lines joining the two atoms. Suppose the mean speed of such a molecule in a gas is 500 m/s and that its kinetic energy of rotation is two thirds of its kinetic energy of translation. Find the average angular velocity of the molecule.
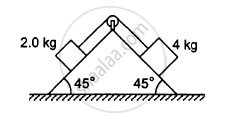
The pulley shown in the following figure has a radius 10 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅5 kg-m2about its axis. Assuming the inclined planes to be frictionless, calculate the acceleration of the 4⋅0 kg block.
A boy is seated in a revolving chair revolving at an angular speed of 120 revolutions per minute. Two heavy balls form part of the revolving system and the boy can pull the balls closer to himself or may push them apart. If by pulling the balls closer, the boy decreases the moment of inertia of the system from 6 kg-m2 to 2 kg-m2, what will be the new angular speed?
A wheel of mass 15 kg has a moment of inertia of 200 kg-m2 about its own axis, the radius of gyration will be:
From a circular ring of mass ‘M’ and radius ‘R’ an arc corresponding to a 90° sector is removed. The moment of inertia of the remaining part of the ring about an axis passing through the centre of the ring and perpendicular to the plane of the ring is ‘K’ times ‘MR2’. Then the value of ‘K’ is ______.
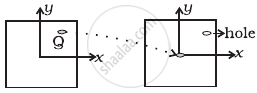
A uniform square plate has a small piece Q of an irregular shape removed and glued to the centre of the plate leaving a hole behind (Figure). The moment of inertia about the z-axis is then ______.
Why does a solid sphere have smaller moment of inertia than a hollow cylinder of same mass and radius, about an axis passing through their axes of symmetry?
Moment of inertia (M.I.) of four bodies, having same mass and radius, are reported as :
I1 = M.I. of thin circular ring about its diameter,
I2 = M.I. of circular disc about an axis perpendicular to disc and going through the centre,
I3 = M.I. of solid cylinder about its axis and
I4 = M.I. of solid sphere about its diameter.
Then -
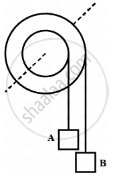
The figure shows a small wheel fixed coaxially on a bigger one of double the radius. The system rotates about the common axis. The strings supporting A and B do not slip on the wheels. If x and y be the distances travelled by A and B in the same time interval, then ______.