Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Benzoyl chloride to benzaldehyde
उत्तर
Conversion of Benzoyl chloride to benzaldehyde:
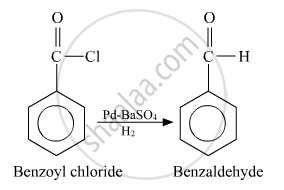
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions : Rosenmund reduction
Ozonolysis of alkenes followed by the reaction with zinc dust and water gives ____________ depending on the substitution pattern of the alkene.
Match the acids given in Column I with their correct IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Acids) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Phthalic acid | (a) | Hexane-1,6-dioic acid |
| (ii) | Oxalic acid | (b) | Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid |
| (iii) | Succinic acid | (c) | Pentane-1,5-dioic acid |
| (iv) | Adipic acid | (d) | Butane-1,4-dioic acid |
| (v) | Glutaric acid | (e) | Ethane-1,2-dioic acid |
An alkene ‘A’ (Mol. formula \[\ce{C5H10}\]) on ozonolysis gives a mixture of two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ gives positive Fehling’s test and also forms iodoform on treatment with \[\ce{I2}\] and \[\ce{NaOH}\]. Compound ‘C’ does not give Fehling’s test but forms iodoform. Identify the compounds A, B and C. Write the reaction for ozonolysis and formation of iodoform from B and C.
An aromatic compound ‘A’ (Molecular formula \[\ce{C8H8O}\]) gives positive 2, 4-DNP test. It gives a yellow precipitate of compound ‘B’ on treatment with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution. Compound ‘A’ does not give Tollen’s or Fehling’s test. On drastic oxidation with potassium permanganate it forms a carboxylic acid ‘C’ (Molecular formula \[\ce{C7H6O2}\]), which is also formed along with the yellow compound in the above reaction. Identify A, B and C and write all the reactions involved.
The strongest base among the following
The number of chiral carbon in glucose is:-
The general formula CnH2NO2 could be for open chain
Reagent used to convert allyl alcohol to acrolein is ______.
An organic compound with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H7NO2}\] exists in three isomeric forms, the isomer ‘A’ has the highest melting point of the three. ‘A’ on reduction gives compound ‘B’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H9N}\]. ‘B’ on treatment with \[\ce{NaNO2/HCl}\] at 0-5° C to form compound ‘C’. On treating C with \[\ce{H3PO2}\], it gets converted to D with formula \[\ce{C7H8}\], which on further reaction with \[\ce{CrO2Cl2}\] followed by hydrolysis forms ‘E’ \[\ce{C7H6O}\]. Write the structure of compounds A to E. Write the chemical equations involved.
