Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How would you account for the following?
Transition metals and their compounds act as catalysts.
Give a Reason for the Following:
Transition Elements and Their Compounds Act as Catalysts.
Explain giving reason:
Transition metals and their many compounds act as good catalysts.
उत्तर
Transition metals and their compounds are known for their catalytic activity. This property of transition metals is due to their variable valency and their ability to form complex compounds. Vanadium (V) oxide (in the contact process), finely divided iron (in the Haber process) and nickel (in catalytic hydrogenation) are some examples of catalysis by transition metals. Bonds are formed between the reactant molecules and the atoms of the catalyst surface on the solid surface of the catalyst. Metals of the first transition series use 3d and 4s electrons to form bonds, as a result of which the concentration of the reactant on the catalyst surface increases and the bonds present in the reactant molecules become weak. Due to this, the value of activation energy decreases. Transition metals are more effective as catalysts because of the possibility of changes in oxidation states.
For example: Iron (III) catalyzes the reaction between the iodide ion and the persulfate ion.
\[\ce{2I^- + S2O^{2-}_8 -> I2 ^ + 2SO^{2-}_4}\]
The explanation of this catalytic reaction is as follows:
\[\ce{2Fe^{3+} + 2I^- -> 2Fe^{2+} + I2 ^}\]
\[\ce{2Fe^{2+} + S2O^{2-}_8 -> 2Fe^{3+} + 2SO^{2-}_4}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Complete the following chemical equations:
`(i) Cr_2O_7^(2-)+6Fe^(2+)+14H^+ ->`
`(ii) 2CrO_4^(2-)+2H^+ ->`
`(iii) 2MnO_4^-+5C_2O_4^(2-)+16H^+ ->`
The elements of 3d transition series are given as: Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co
Answer the following: Which element shows only +3 oxidation state?
How would you account for the following: Transition metals form complex compounds.
Account for the following:
Cu+ ion is unstable in aqueous solution.
Explain briefly how +2 state becomes more and more stable in the first half of the first row transition elements with increasing atomic number?
In what way is the electronic configuration of the transition elements different from that of the non-transition elements?
Compare the stability of +2 oxidation state for the elements of the first transition series.
How would you account for the following:
Cobalt (II) is stable in aqueous solutions, but in the presence of complexing reagents, it is easily oxidised.
How would you account for the following:
The d1 configuration is very unstable in ions.
What are alloys?
Write the factors which are related to the colour of transition metal ions.
NF3 is possible, but NF5 is not. Why?
The magnetic nature of elements depends on the presence of unpaired electrons. Identify the configuration of transition element, which shows highest magnetic moment.
Transition elements show high melting points. Why?
Out of \[\ce{Cu2Cl2}\] and \[\ce{CuCl2}\], which is more stable and why?
The second and third rows of transition elements resemble each other much more than they resemble the first row. Explain why?
Answer the following question:
Which element of the first transition series has highest second ionisation enthalpy?
Mention any three processes where transition metals act as catalysts.
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the following questions:
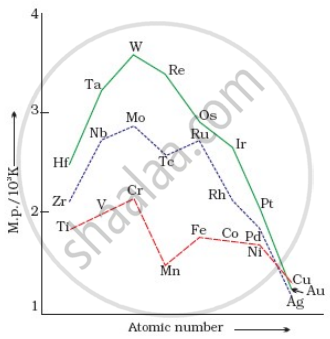
- Why Manganese has lower melting point than Chromium?
- Why do transition metals of 3d series have lower melting points as compared to 4d series?
- In the third transition series, identify and name the metal with the highest melting point.
A metallic ion 'M' reacts with chloride ion to form white precipitate which is readily soluble in aqueous ammonia. Identify 'M'?
The element with atomic number 46 belongs to
The standard electrode potentials of four elements A, B, C and D are – 3.05, – 1.66, – 0.40 and + 0.80. The highest chemical reactivity will be exhibited by
Among the following pairs of ions, the lower oxidation state in aqueous solution is more stable than the other in:-
The value of Δ0 for \[\ce{RhCl^{3-}6}\] is 243 KJ/mol which wavelength of light will promote an electron from. The colour of the complex is ______.
Which property of transition metals enables them to behave as catalysts?
Which of the following ions has the electronic configuration 3d6?
(Atomic number: Mn = 25, Co = 27, Ni = 28)
Describe the oxidising action of potassium dichromate and write the ionic equation for its reaction with H2S.
