Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In fig common tangents PQ and RS to two circles intersect at A. Prove that PQ = RS.
उत्तर
Consider
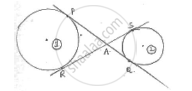
Two circles namely (i) & (ii) as shown with common tangents as PQ and RS.
We know that
The tangents from external point to the circle are equal in length.
From A to circle (i) AP = AR … (i)
From A to circle (ii), AQ = AS …. (ii)
(i) + (ii) ⇒ AP + AQ = AR + RS
⇒ PQ = RS
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the length of a tangent drawn to a circle with radius 5cm, from a point 13 cm from the center of the circle.
From a point P, two tangents PA and PB are drawn to a circle with center O. If OP =
diameter of the circle shows that ΔAPB is equilateral.
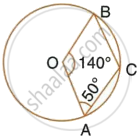
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. If ∠AOB = 140° and ∠OAC = 50°; find:
- ∠ACB,
- ∠OBC,
- ∠OAB,
- ∠CBA.
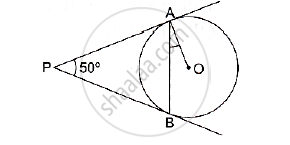
In the given figure, PA and PB are two tangents to the circle with centre O. If ∠APB = 50° then what is the measure of ∠OAB.
In the given figure, if ∠ABC = 45°, then ∠AOC =
In the given figure, the area enclosed between the two concentric circles is 770 cm2. If the radius of the outer circle is 21 cm, calculate the radius of the inner circle.
Draw circle with diameter: 6 cm
In above case, measure the length of the radius of the circle drawn.
State, if the following statement is true or false:
The diameters of a circle always pass through the same point in the circle.
Two circles with centres O and O' of radii 3 cm and 4 cm, respectively intersect at two points P and Q such that OP and O'P are tangents to the two circles. Find the length of the common chord PQ.
Two chords AB and AC of a circle subtends angles equal to 90º and 150º, respectively at the centre. Find ∠BAC, if AB and AC lie on the opposite sides of the centre.
