Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the following figures, ABCD is a parallelogram.

Find the values of x and y.
उत्तर
In the figure, ABCD is a parallelogram
∠D = ∠B ...[Since opposite angles are equal.]
6x + 3y - 8 = 7y
6x + 3y - 7y = 8
6x - 4y = 8
2(3x - 2y) = 8
3x - 2y = 4 ...(i)
∠A + ∠B = 180°
4x + 20° + 7y = 180°
4x + 7y = 160° ...(ii)
Multiply by equation (i) × 4 and equation (ii) × 3
12x - 8y = 16
12x + 21y = 480
- - -
- 29y = - 464
y = `(- 464)/(- 29)`
y = 16
Put y = 16 in equation (i)
∴ 3x - 2y = 4
⇒ 3x - 2(16) = 4
⇒ 3x - 32 = 4
⇒ 3x = 4 + 32
⇒ 3x = 36
⇒ x = `36/3`
⇒ x = 12
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the diagonals of a parallelogram are equal, then show that it is a rectangle.
ABCD is a rectangle in which diagonal AC bisects ∠A as well as ∠C. Show that:
- ABCD is a square
- diagonal BD bisects ∠B as well as ∠D.
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || CD and AD = BC (see the given figure). Show that
- ∠A = ∠B
- ∠C = ∠D
- ΔABC ≅ ΔBAD
- diagonal AC = diagonal BD
[Hint: Extend AB and draw a line through C parallel to DA intersecting AB produced at E.]
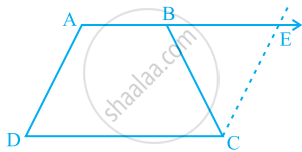
State, 'true' or 'false'
The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other at right angle.
State, 'true' or 'false'
Each diagonal of a rhombus bisects it.
The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 3: 4: 5: 6. Show that the quadrilateral is a trapezium.
State, 'true' or 'false'
If the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angle, the quadrilateral is a square.
In the given figure ABCD is a rhombus with angle A = 67°

If DEC is an equilateral triangle, calculate:
- ∠CBE
- ∠DBE
PQRS is a rectangle in which PQ = 12cm and PS = 8cm. Calculate the area of ΔPRS.
In the figure, PT is parallel to SR. QTSR is a parallelogram and PQSR is a rectangle. If the area of ΔQTS is 60cm2, find:
(i) the area o || gm QTSR
(ii) the area of the rectangle PQRS
(iii) the area of the triangle PQS.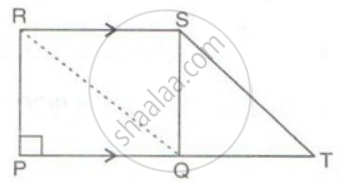
AD is a median of a ΔABC.P is any point on AD. Show that the area of ΔABP is equal to the area of ΔACP.
If the medians of a ΔABBC intersect at G, show that ar(ΔAGB) = ar(ΔAGC) = ar(ΔBGC) = `(1)/(3)"ar(ΔABC)"`.
Find the area of a parallelogram whose base is 12cm and the height is 5cm.
Find the height of a parallelogram whose area is 144cm2 and the base is 18cm.
The side of a square exceeds the side of another square by 4cm and the sum of the areas of the squares is 400cm2. Find the dimensions of the squares.
The area of a rhombus is 234 cm2. If its one diagonal is 18 cm, find the lengths of its side and the other diagonal. Also, find perimeter of the rhombus.
A rectangular field is 240m long and 180m broad. In one corner a farm house is built on a square plot of side 40m. Find the area of the remaining portion and the cost of fencing the open sides Rs.25per m.
The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length.
Give reason for the following :
Square is also a parallelogram.
