Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the given figure ABCD is a rhombus with angle A = 67°

If DEC is an equilateral triangle, calculate:
- ∠CBE
- ∠DBE
उत्तर
Given that the figure ABCD is a rhombus with angle A = 67o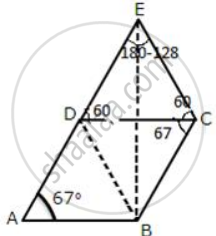
In the rhombus we have
∠A = 67° = ∠C ...[Opposite angles]
∠A + ∠D = 180° ...[Consecutive angles are supplementary.]
⇒ ∠D = 113°
⇒ ∠ABC = 113°
Consider ΔDBC,
DC = CB ...[Sides of rhombus]
So, ΔDBC is an isosceles triangle,
⇒ ∠CDB = ∠CBD
Also,
∠CDB + ∠CBD + ∠BCD = 180°
⇒ 2∠CBD = 113°
⇒ ∠CDB = ∠CBD = 56.5° ...(i)
Consider ΔDCE,
EC = CB
So ΔBCE is an isosceles triangle
⇒ ∠CBE = ∠CEB
Also,
∠CBE + ∠CEB + ∠BCE = 180°
⇒ 2∠CBE = 53°
⇒ ∠CDE = 26.5°
From (i)
∠CBD = 56.5°
⇒ ∠CBE + ∠DBE = 56.5°
⇒ 26.5° + ∠DBE = 56.5°
⇒ ∠DBE = 56.5° - 26.5°
⇒ ∠DBE = 30°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the diagonals of a parallelogram are equal, then show that it is a rectangle.
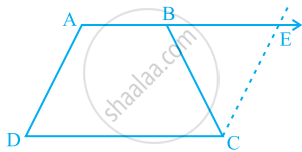
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || CD and AD = BC (see the given figure). Show that
- ∠A = ∠B
- ∠C = ∠D
- ΔABC ≅ ΔBAD
- diagonal AC = diagonal BD
[Hint: Extend AB and draw a line through C parallel to DA intersecting AB produced at E.]
State, 'true' or 'false'
Each diagonal of a rhombus bisects it.
State, 'true' or 'false'
The quadrilateral, whose four sides are equal, is a square.
The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 3: 4: 5: 6. Show that the quadrilateral is a trapezium.
In the following figures, ABCD is a parallelogram.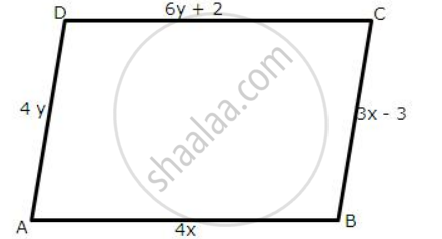
find the values of x and y.
In the given figure, ST ∥ PR. Prove that: area of quadrilateral PQRS = area of ΔPQT.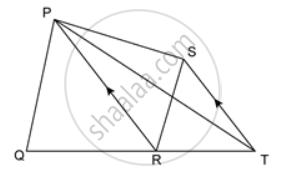
The diagonals of a parallelogram ABCD intersect at O. A line through O meets AB in P and CD in Q. Show that
(a) Area of APQD = `(1)/(2)` area of || gm ABCD
(b) Area of APQD = Area of BPQC
In the given figure, BC ∥ DE.
(a) If area of ΔADC is 20 sq. units, find the area of ΔAEB.
(b) If the area of ΔBFD is 8 square units, find the area of ΔCEF
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle and AD is the median.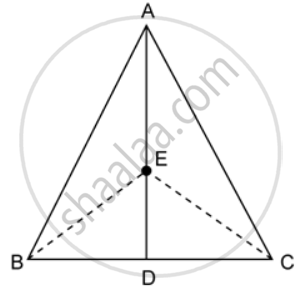
If E is the midpoint of the median AD, prove that: Area of ΔABC = 4 × Area of ΔABE
The area of a square garden is equal to the area of a rectangular plot of length 160m and width 40m. Calculate the cost of fencing the square garden at Rs.12per m.
Find the perimeter and area of a square whose diagonal is `5sqrt(2)"cm"`. Give your answer correct to two decimal places if `sqrt(2)` = 1.414.
How many tiles, each of area 625 cm2, will be needed to pave a footpath which is 1 m wide and surrounds a grass plot of size 38 m x 14 m?
The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length.
All the sides of a rhombus are of equal length.
Give reasons for the following :
A rectangle can be thought of as a special parallelogram.
Examine whether the following is a polygon. If it is not, say why?

