Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
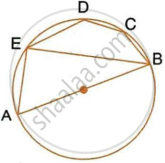
In the given figure, AB is a diameter of the circle. Chord ED is parallel to AB and ∠EAB = 63°.
Calculate:
- ∠EBA,
- ∠BCD.
उत्तर
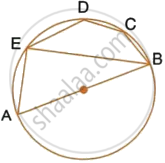
i. ∠AEB = 90°
(Angle in a semicircle is a right angle)
Therefore ∠EBA = 90° – ∠EAB
= 90° – 63°
= 27°
ii. AB || ED
Therefore ∠DEB = ∠EBA = 27° (Alternate angles)
Therefore BCDE is a cyclic quadrilateral
Therefore ∠DEB + ∠BCD = 180°
[Pair of opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary]
Therefore ∠BCD = 180° – 27° = 153°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
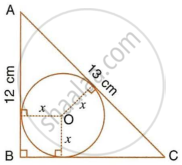
ABC is a right angles triangle with AB = 12 cm and AC = 13 cm. A circle, with centre O, has been inscribed inside the triangle.
Calculate the value of x, the radius of the inscribed circle.
Two circles intersect at P and Q. Through P diameters PA and PB of the two circles are drawn. Show that the points A, Q and B are collinear.
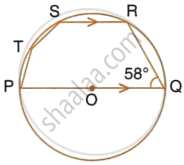
In the given figure, PQ is a diameter. Chord SR is parallel to PQ. Given that ∠PQR = 58°,
Calculate:
- ∠RPQ,
- ∠STP.
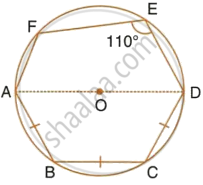
In the following figure, AD is the diameter of the circle with centre O. Chords AB, BC and CD are equal. If ∠DEF = 110°, calculate: ∠AEF
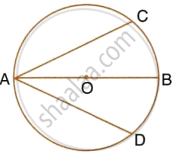
In the given figure, AB is the diameter of a circle with centre O.
If chord AC = chord AD, prove that:
- arc BC = arc DB
- AB is bisector of ∠CAD.
Further, if the length of arc AC is twice the length of arc BC, find:
- ∠BAC
- ∠ABC
Using ruler and a compass only construct a semi-circle with diameter BC = 7cm. Locate a point A on the circumference of the semicircle such that A is equidistant from B and C. Complete the cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, such that D is equidistant from AB and BC. Measure ∠ADC and write it down.
In the given figure, AB is a diameter of the circle. Chord ED is parallel to AB and ∠EAB = 63°. Calculate : ∠BCD.
In the given figure, AB is a diameter of the circle with centre O. DO is parallel to CB and ∠DCB = 120°.
Calculate : ∠ADC
Also, show that the ΔAOD is an equilateral triangle.
In the figure given alongside, AD is the diameter of the circle. If ∠ BCD = 130°, Calculate: (i) ∠ DAB (ii) ∠ ADB.