Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
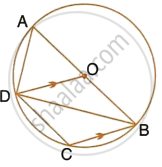
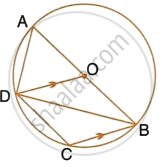
In the given figure, AB is a diameter of the circle with centre O. DO is parallel to CB and ∠DCB = 120°.
Calculate : ∠ADC
Also, show that the ΔAOD is an equilateral triangle.
उत्तर
∠ABD + ∠DBC = 30° + 30° = 60°
`=>` ∠ABC = 60°
In cyclic quadrilateral ABCD,
∠ADC + ∠ABC = 180°
(Pair of opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary)
`=>` ∠ADC = 180° – 60° = 120°
In ∆AOD, OA = OD (Radii of the same circle)
∠AOD = ∠DAO Or ∠DAB = 60° [Proved in (i)]
∠AOD = 60°
`=>` ∠ADO = ∠AOD = ∠DAO = 60°
∴ ∆AOD is an equilateral triangle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the figure, m∠DBC = 58°. BD is the diameter of the circle. Calculate:
1) m∠BDC
2) m∠BEC
3) m∠BAC
Calculate the area of the shaded region, if the diameter of the semicircle is equal to 14 cm. Take `pi = 22/7`

In the figure, given alongside, AB || CD and O is the centre of the circle. If ∠ADC = 25°; find the angle AEB. Give reasons in support of your answer.

In the given figure, AB is a diameter of the circle. Chord ED is parallel to AB and ∠EAB = 63°.
Calculate:
- ∠EBA,
- ∠BCD.
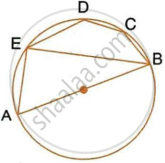
Prove that the circle drawn on any one of the equal sides of an isosceles triangle as diameter bisects the base.
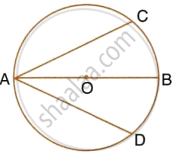
In the given figure, AB is the diameter of a circle with centre O.
If chord AC = chord AD, prove that:
- arc BC = arc DB
- AB is bisector of ∠CAD.
Further, if the length of arc AC is twice the length of arc BC, find:
- ∠BAC
- ∠ABC
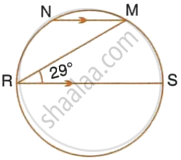
In the given figure, RS is a diameter of the circle. NM is parallel to RS and ∠MRS = 29°. Calculate : ∠NRM
In the given figure, AB is a diameter of the circle with centre O. DO is parallel to CB and ∠DCB = 120°.
Calculate : ∠DBC
Also, show that the ΔAOD is an equilateral triangle.

In the figure, ∠DBC = 58°. BD is diameter of the circle.
Calculate:
- ∠BDC
- ∠BEC
- ∠BAC
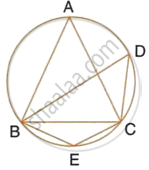
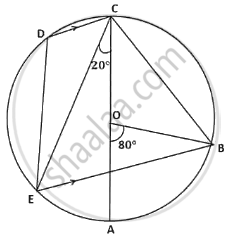
In the given figure AC is the diameter of the circle with centre O. CD is parallel to BE.
∠AOB = 80° and ∠ACE = 20°.
Calculate
- ∠BEC
- ∠BCD
- ∠CED