Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
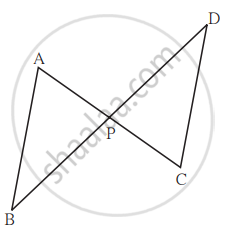
In the given figure, seg AC and seg BD intersect each other in point P and `"AP"/"CP" = "BP"/"DP"`. Prove that, ∆ABP ~ ∆CDP.
उत्तर
Given: Seg AC and seg BD intersect each other in point P and `"AP"/"CP" = "BP"/"DP"`.
To prove: ∆ABP ~ ∆CDP
Proof: In ∆ABP and ∆CDP,
`"AP"/"CP" = "BP"/"DP"` ...(Given)
∠APB ≅ ∠CPD ...(vertically opposite angles)
By SAS test of similarity,
∆ABP ~ ∆CDP
Hence Proved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
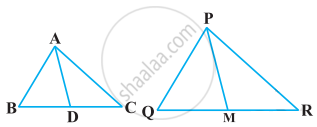
In the following figure, `("QR")/("QS") = ("QT")/("PR")` and ∠1 = ∠2. Show that ΔPQS ~ ΔTQR.
In the following figure, altitudes AD and CE of ΔABC intersect each other at the point P. Show that:
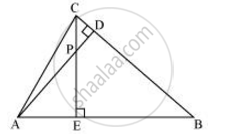
ΔAEP ∼ ΔCDP
In the following figure, altitudes AD and CE of ΔABC intersect each other at the point P. Show that:
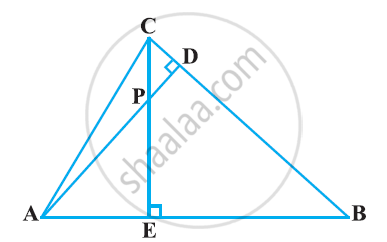
ΔAEP ∼ ΔADB
In the following figure, altitudes AD and CE of ΔABC intersect each other at the point P. Show that:
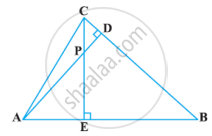
ΔPDC ∼ ΔBEC
If AD and PM are medians of triangles ABC and PQR, respectively where ΔABC ~ ΔPQR, prove that `("AB")/("PQ") = ("AD")/("PM")`.
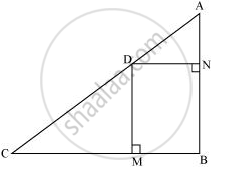
In the given figure, D is a point on hypotenuse AC of ΔABC, DM ⊥ BC and DN ⊥ AB, Prove that:
(i) DM2 = DN.MC
(ii) DN2 = DM.AN
A vertical stick 10 cm long casts a shadow 8 cm long. At the same time a shadow 30 m long. Determine the height of the tower.
The sides of certain triangles are given below. Determine which of them right triangles are.
1.4cm, 4.8cm, 5cm
Two triangles ABC and PQR are such that AB = 3 cm, AC = 6cm, ∠𝐴 = 70°, PR = 9cm ∠𝑃 = 70° and PQ = 4.5 cm. Show that ΔABC ∼ΔPQR and state that similarity criterion.
Two triangles DEF an GHK are such that ∠D = 48° and ∠H = 57° . If ΔDEF ∼GHK then find the measures of ∠F
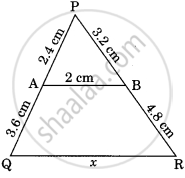
In the given figure, value of x(in cm) is
If ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF, AB = 4 cm, DE = 6 cm, EF = 9 cm and FD = 12 cm, find the perimeter of ∆ABC.
In the figure, if ∠ACB = ∠CDA, AC = 8 cm and AD = 3 cm, find BD.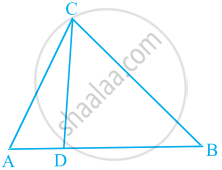
It is given that ΔABC ~ ΔDFE, ∠A =30°, ∠C = 50°, AB = 5 cm, AC = 8 cm and DF = 7.5 cm. Then, the following is true ______.
Which of the following conditions is not sufficient to determine the congruence of two triangles?
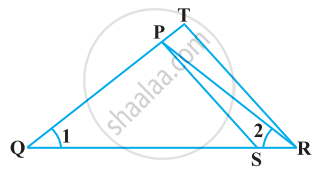
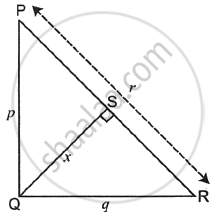
In the given figure, ΔPQR is a right-angled triangle with ∠PQR = 90°. QS is perpendicular to PR. Prove that pq = rx.
The sum of two angles of a triangle is 150°, and their difference is 30°. Find the angles.
In the given figure, DE ∥ BC, AE = a units, EC = b units, DE = x units and BC = y units. Which of the following is true?
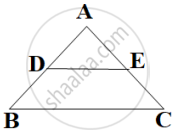
If ΔABC ~ ΔDEF and ∠A = 47°, ∠E = 83°, then ∠C is equal ______.
Sides AB and BC and median AD of a triangle ABC are respectively proportional to sides PQ and QR and median PM of ΔPQR show that ΔABC ~ ΔPQR.