Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
[NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic though both are tetrahedral. Why? (Atomic no. Ni = 28)
उत्तर
[NiCl4]2-
Ni is in + 2 oxidation state.
3d8 configuration 
Cl- is weak field ligand. So, pairing doesnot occur.
sp3 hybridised orbitals of 2 Ni2+ 

[ ] NiCl is paramagnetic as n = 2
4 [ ( ) ] Ni CO Ni is in ‘0’ oxidation state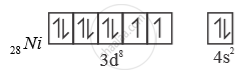
In presence of ‘CO’ pairing of e– takes place ‘CO’ is strong field ligand. So, with ‘CO
[Ni(CO)4] → 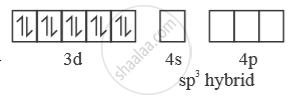
[Ni(CO)4] → 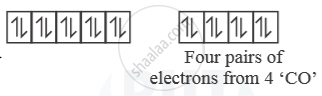
So, [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic as n = 0.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain on the basis of valence bond theory that [Ni(CN)4]2− ion with square planar structure is diamagnetic and the [NiCl4]2− ion with tetrahedral geometry is paramagnetic.
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entity on the basis of valence bond theory:
[FeF6]3−
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entity on the basis of valence bond theory:
[Co(C2O4)3]3−
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[Cr(H2O)6]^{3+}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[FeCl6]^{4-}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
Which of the following has square planar structures?
What is the no. of possible isomers for the octahedral complex [Co(NH3)2(C2O4)2]?
In Fe(CO)5, the Fe – C bond possesses
Using valence bond theory, predict the hybridization and magnetic character of the following:
[CoF6]3– [Atomic number of Co = 27]
[Ni(CO)4] has tetrahedral geometry while [Ni(CN)4]2− has square planar, yet both exhibit diamagnetism. Explain.
[Atomic number: Ni = 28]
