Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State exterior angle theorem.
उत्तर
Exterior angle theorem states that, if a side of a triangle is produced, the exterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles.
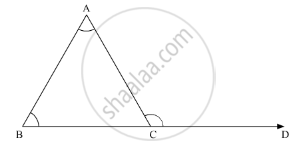
Thus, in ΔABC
∠ACD = ∠A +∠B
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the given figure, AC ⊥ CE and ∠A : ∠B : ∠C = 3 : 2 : 1, find the value of ∠ECD.
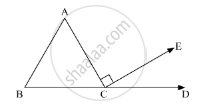
Is the following statement true and false :
A triangle can have two right angles.
If one angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the other two angles, then the triangle is
The bisects of exterior angle at B and C of ΔABC meet at O. If ∠A = x°, then ∠BOC =
State, if the triangle is possible with the following angles :
60°, 60°, and 50°
Can a triangle together have the following angles?
55°, 55° and 80°
Can a triangle together have the following angles?
33°, 74° and 73°
P is a point on the bisector of ∠ABC. If the line through P, parallel to BA meet BC at Q, prove that BPQ is an isosceles triangle.
In figure, ∠BAC = 90° and AD ⊥ BC. The number of right triangles in the figure is ______.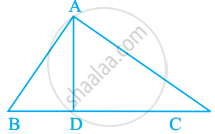
Can we have two acute angles whose sum is an obtuse angle? Why or why not?
